Contexts for dopamine specification by calcium spike activity in the CNS
- PMID: 21209192
- PMCID: PMC3080040
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3542-10.2011
Contexts for dopamine specification by calcium spike activity in the CNS
Abstract
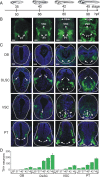
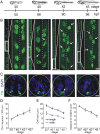
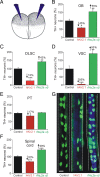
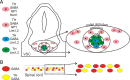
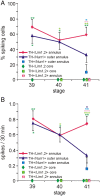
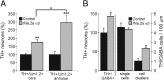
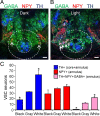
Calcium-dependent electrical activity plays a significant role in neurotransmitter specification at early stages of development. To test the hypothesis that activity-dependent differentiation depends on molecular context, we investigated the development of dopaminergic neurons in the CNS of larval Xenopus laevis. We find that different dopaminergic nuclei respond to manipulation of this early electrical activity by ion channel misexpression with different increases and decreases in numbers of dopaminergic neurons. Focusing on the ventral suprachiasmatic nucleus and the spinal cord to gain insight into these differences, we identify distinct subpopulations of neurons that express characteristic combinations of GABA and neuropeptide Y as cotransmitters and Lim1,2 and Nurr1 transcription factors. We demonstrate that the developmental state of neurons identified by their spatial location and expression of these molecular markers is correlated with characteristic spontaneous calcium spike activity. Different subpopulations of dopaminergic neurons respond differently to manipulation of this early electrical activity. Moreover, retinohypothalamic circuit activation of the ventral suprachiasmatic nucleus recruits expression of dopamine selectively in reserve pool neurons that already express GABA and neuropeptide Y. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that spontaneously active neurons expressing GABA are most susceptible to activity-dependent expression of dopamine in both the spinal cord and brain. Because loss of dopaminergic neurons plays a role in neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease, understanding how subpopulations of neurons become dopaminergic may lead to protocols for differentiation of neurons in vitro to replace those that have been lost in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Abalo XM, Villar-Cheda B, Anadón R, Rodicio MC. Development of the dopamine-immunoreactive system in the central nervous system of the sea lamprey. Brain Res Bull. 2005;66:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Abbott LC, Isaacs KR, Heckroth JA. Co-localization of tyrosine hydroxylase and zebrin II immunoreactivities in Purkinje cells of the mutant mice, tottering and tottering/leaner. Neuroscience. 1996;71:461–475. - PubMed
-
- Ang SL. Transcriptional control of midbrain dopaminergic neuron development. Development. 2006;133:3499–3506. - PubMed
-
- Appel B, Korzh V, Glasgow E, Thor S, Edlund T, Dawid IB, Eisen JS. Motoneuron fate specification revealed by patterened LIM homeobox gene expression in embryonic zebrafish. Development. 1995;121:4117–4125. - PubMed
-
- Austin MC, Schultzberg M, Abbott LC, Montpied P, Evers JR, Paul SM, Crawley JN. Expression of tyrosine hydroxylase in cerebellar Purkinje neurons of the mutant tottering and leaner mouse. Mol Brain Res. 1992;15:227–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
