1, 9-Pyrazoloanthrones downregulate HIF-1α and sensitize cancer cells to cetuximab-mediated anti-EGFR therapy
- PMID: 21209911
- PMCID: PMC3012113
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015823
1, 9-Pyrazoloanthrones downregulate HIF-1α and sensitize cancer cells to cetuximab-mediated anti-EGFR therapy
Abstract
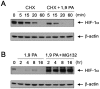
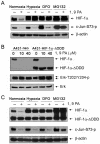
Cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody that blocks the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), is currently approved for the treatment of several types of solid tumors. We previously showed that cetuximab can inhibit hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) protein synthesis by inhibiting the activation of EGFR downstream signaling pathways including Erk, Akt, and mTOR. 1, 9-pyrazoloanthrone (1, 9 PA) is an anthrapyrazolone compound best known as SP600125 that specifically inhibits c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Here, we report 1, 9 PA can downregulate HIF-1α independently of its inhibition of JNK. This downregulatory effect was abolished when the oxygen-dependent domain (ODD) of HIF-1α (HIF-1α-ΔODD, the domain responsible for HIF-1α degradation) was experimentally deleted or when the activity of HIF-1α prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) or the 26S proteasomal complex was inhibited, indicating that the 1, 9 PA downregulates HIF-1α by promoting PHD-dependent HIF-1α degradation. We found that the combination of 1, 9 PA and cetuximab worked synergistically to induce apoptosis in cancer cells in which cetuximab or 1, 9 PA alone had no or only weak apoptotic activity. This synergistic effect was substantially decreased in cancer cells transfected with HIF-1α-ΔODD, indicating that downregulation of HIF-1α was the mechanism of this synergistic effect. More importantly, 1, 9 PA can downregulate HIF-1α in cancer cells that are insensitive to cetuximab-induced inhibition of HIF-1α expression due to overexpression of oncogenic Ras (RasG12V). Our findings suggest that 1, 9 PA is a lead compound of a novel class of drugs that may be used to enhance the response of cancer cells to cetuximab through a complementary effect on the downregulation of HIF-1α.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

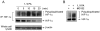
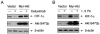
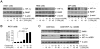
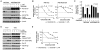
Similar articles
-
Responses of cancer cells with wild-type or tyrosine kinase domain-mutated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to EGFR-targeted therapy are linked to downregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha.Mol Cancer. 2007 Oct 11;6:63. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-6-63. Mol Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17931419 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha down-regulation in mediating the antitumor activity of the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 May;7(5):1207-17. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2187. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18483308
-
The antiepidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab/C225 reduces hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha, leading to transcriptional inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor expression.Oncogene. 2005 Jun 23;24(27):4433-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208625. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15806152
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006 Jan;1(1):1-13. doi: 10.2174/157488706775246157. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006. PMID: 18393776 Review.
-
Cetuximab: from bench to bedside.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010 Feb;10(1):80-95. doi: 10.2174/156800910790980241. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20088790 Review.
Cited by
-
AP1G1 is involved in cetuximab-mediated downregulation of ASCT2-EGFR complex and sensitization of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to ROS-induced apoptosis.Cancer Lett. 2017 Nov 1;408:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28823958 Free PMC article.
-
Melittin suppresses HIF-1α/VEGF expression through inhibition of ERK and mTOR/p70S6K pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 23;8(7):e69380. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069380. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936001 Free PMC article.
-
Functional cooperation between HIF-1α and c-Jun in mediating primary and acquired resistance to gefitinib in NSCLC cells with activating mutation of EGFR.Lung Cancer. 2018 Jul;121:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.04.024. Epub 2018 May 1. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29858032 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab sensitizes human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to radiation in part through inhibiting radiation-induced upregulation of HIF-1α.Cancer Lett. 2012 Sep 1;322(1):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Cancer Lett. 2012. PMID: 22348829 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutively active Harvey Ras confers resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy with cetuximab and gefitinib.Cancer Lett. 2011 Jul 1;306(1):85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.02.035. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21411223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schlessinger J. Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor. Cell. 2002;110:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2000;19:6550–6565. - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello F, Tortora G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1160–1174. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:337–345. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Trigo JM, Bourhis J, Tortochaux J, Cortes-Funes H, et al. Phase II multicenter study of the antiepidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with platinum-refractory metastatic and/or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5568–5577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

