NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species mediate FFAs-induced dysfunction and apoptosis of β-cells via JNK, p38 MAPK and p53 pathways
- PMID: 21209957
- PMCID: PMC3012098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015726
NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species mediate FFAs-induced dysfunction and apoptosis of β-cells via JNK, p38 MAPK and p53 pathways
Abstract
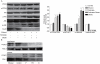
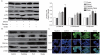
Dysfunction of β-cell is one of major characteristics in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. The combination of obesity and type 2 diabetes, characterized as 'diabesity', is associated with elevated plasma free fatty acids (FFAs). Oxidative stress has been implicated in the pathogenesis of FFA-induced β-cell dysfunction. However, molecular mechanisms linking between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and FFA-induced β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis are less clear. In the present study, we test the hypothesis that NOX2-derived ROS may play a critical role in dysfunction and apoptosis of β-cells induced by FFA. Our results show that palmitate and oleate (0.5 mmol/L, 48 h) induced JNK activation and AKT inhibition which resulted in decreased phosphorylation of FOXO1 following nuclear localization and the nucleocytoplasmic translocation of PDX-1, leading to the reducing of insulin and ultimately dysfunction of pancreatic NIT-1 cells. We also found that palmitate and oleate stimulated apoptosis of NIT-1 cells through p38MAPK, p53 and NF-κB pathway. More interestingly, our data suggest that suppression of NOX2 may restore FFA-induced dysfunction and apoptosis of NIT-1 cells. Our findings provide a new insight of the NOX2 as a potential new therapeutic target for preservation of β-cell mass and function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

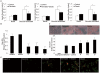

Similar articles
-
NADPH oxidase 2 plays a critical role in dysfunction and apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells induced by very low-density lipoprotein.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Nov;370(1-2):103-13. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1402-z. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22911512
-
NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species are involved in dysfunction and apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells induced by low density lipoprotein.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(2):439-49. doi: 10.1159/000339037. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22814241
-
The effects of palmitate on hepatic insulin resistance are mediated by NADPH Oxidase 3-derived reactive oxygen species through JNK and p38MAPK pathways.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 24;285(39):29965-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.128694. Epub 2010 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20647313 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Roles of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Pathways in Health and Diabetes: Lessons Learned from the Pancreatic β-Cell.Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2017;10(2):76-84. doi: 10.2174/1872214810666161020154905. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 27779078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NADPH Oxidase (NOX) Targeting in Diabetes: A Special Emphasis on Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction.Cells. 2021 Jun 22;10(7):1573. doi: 10.3390/cells10071573. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34206537 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Obesity-Related Lipotoxicity and Clinical Perspective.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:131-166. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287851 Review.
-
Saturated free fatty acids induce cholangiocyte lipoapoptosis.Hepatology. 2014 Dec;60(6):1942-56. doi: 10.1002/hep.27175. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 24753158 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidases: redox regulation of cell homeostasis and disease.Physiol Rev. 2025 Jul 1;105(3):1291-1428. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00034.2023. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Physiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39814410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of tumor suppressor p53 preserves glycation-serum induced pancreatic beta-cell demise.Endocrine. 2016 Nov;54(2):383-395. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0979-5. Epub 2016 May 9. Endocrine. 2016. PMID: 27160820
-
Identification of core genes associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and gastric cancer by bioinformatics analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Mar;10(5):247. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3635. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35402578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guillausseau PJ, Meas T, Virally M, Laloi-Michelin M, Medeau V, et al. Abnormalities in insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34(Suppl 2):S43–48. - PubMed
-
- Bikopoulos G, da Silva Pimenta A, Lee SC, Lakey JR, Der SD, et al. Ex vivo transcriptional profiling of human pancreatic islets following chronic exposure to monounsaturated fatty acids. J Endocrinol. 2008;196:455–464. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Grill V. Long term exposure to fatty acids and ketones inhibits B-cell functions in human pancreatic islets of Langerhans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:1584–1590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

