Ciliopathies: an expanding disease spectrum
- PMID: 21210154
- PMCID: PMC3098370
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-010-1731-7
Ciliopathies: an expanding disease spectrum
Abstract
Ciliopathies comprise a group of disorders associated with genetic mutations encoding defective proteins, which result in either abnormal formation or function of cilia. As cilia are a component of almost all vertebrate cells, cilia dysfunction can manifest as a constellation of features that include characteristically, retinal degeneration, renal disease and cerebral anomalies. Additional manifestations include congenital fibrocystic diseases of the liver, diabetes, obesity and skeletal dysplasias. Ciliopathic features have been associated with mutations in over 40 genes to date. However, with over 1,000 polypeptides currently identified within the ciliary proteome, several other disorders associated with this constellation of clinical features will likely be ascribed to mutations in other ciliary genes. The mechanisms underlying many of the disease phenotypes associated with ciliary dysfunction have yet to be fully elucidated. Several elegant studies have crucially demonstrated the dynamic ciliary localisation of components of the Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways during signal transduction. Given the critical role of the cilium in transducing "outside-in" signals, it is not surprising therefore, that the disease phenotypes consequent to ciliary dysfunction are a manifestation of aberrant signal transduction. Further investigation is now needed to explore the developmental and physiological roles of aberrant signal transduction in the manifestation of ciliopathy phenotypes. Utilisation of conditional and inducible murine models to delete or overexpress individual ciliary genes in a spatiotemporal and organ/cell-specific manner should help clarify some of the functional roles of ciliary proteins in the manifestation of phenotypic features.
Figures



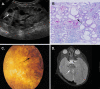

References
-
- Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Blacque OE, Hill J, Hoskins BE, Leitch CC, Kim JC, Ross AJ, Eichers ER, Teslovich TM, Mah AK, Johnsen RC, Cavender JC, Lewis RA, Leroux MR, Beales PL, Katsanis N. Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nature. 2003;425(6958):628–633. - PubMed
-
- Li JB, Gerdes JM, Haycraft CJ, Fan Y, Teslovich TM, May-Simera H, Li H, Blacque OE, Li L, Leitch CC, Lewis RA, Green JS, Parfrey PS, Leroux MR, Davidson WS, Beales PL, Guay-Woodford LM, Yoder BK, Stormo GD, Katsanis N, Dutcher SK. Comparative genomics identifies a flagellar and basal body proteome that includes the BBS5 human disease gene. Cell. 2004;117(4):541–552. - PubMed
-
- Gherman A, Davis EE, Katsanis N. The ciliary proteome database: an integrated community resource for the genetic and functional dissection of cilia. Nat Genet. 2006;38(9):961–962. - PubMed
-
- Beales PL, Bland E, Tobin JL, Bacchelli C, Tuysuz B, Hill J, Rix S, Pearson CG, Kai M, Hartley J, Johnson C, Irving M, Elcioglu N, Winey M, Tada M, Scambler PJ. IFT80, which encodes a conserved intraflagellar transport protein, is mutated in Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy. Nat Genet. 2007;39(6):727–729. - PubMed
-
- Nonaka S, Tanaka Y, Okada Y, Takeda S, Harada A, Kanai Y, Kido M, Hirokawa N. Randomization of left-right asymmetry due to loss of nodal cilia generating leftward flow of extraembryonic fluid in mice lacking KIF3B motor protein. Cell. 1998;95(6):829–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

