NKG2D expression in CD4+ T lymphocytes as a marker of senescence in the aged immune system
- PMID: 21210234
- PMCID: PMC3220398
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-010-9200-6
NKG2D expression in CD4+ T lymphocytes as a marker of senescence in the aged immune system
Abstract
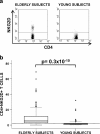
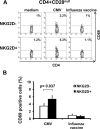
Human aging is characterized by changes in the immune system which have a profound impact on the T-cell compartment. These changes are more frequently found in CD8+ T cells, and there are not well-defined markers of differentiation in the CD4+ subset. Typical features of cell immunosenescence are characteristics of pathologies in which the aberrant expression of NKG2D in CD4+ T cells has been described. To evaluate a possible age-related expression of NKG2D in CD4+ T cells, we compared their percentage in peripheral blood from 100 elderly and 50 young adults. The median percentage of CD4+ NKG2D+ in elders was 5.3% (interquartile range (IR): 8.74%) versus 1.4% (IR: 1.7%) in young subjects (p < 0.3 × 10(-10)). CD28 expression distinguished two subsets of CD4+ NKG2D+ cells with distinct functional properties and differentiation status. CD28+ cells showed an immature phenotype associated with high frequencies of CD45RA and CD31. However, most of the NKG2D+ cells belonged to the CD28(null) compartment and shared their phenotypical properties. NKG2D+ cells represented a more advanced stage of maturation and exhibited greater response to CMV (5.3 ± 3.1% versus 3.4 ± 2%, p = 0.037), higher production of IFN-γ (40.56 ± 13.7% versus 24 ± 8.8%, p = 0.015), lower activation threshold and reduced TREC content. Moreover, the frequency of the CD4+ NKG2D+ subset was clearly related to the status of the T cells. Higher frequencies of the NKG2D+ subset were accompanied with a gradual decrease of NAIVE and central memory cells, but also with a higher level of more differentiated subsets of CD4+ T cells. In conclusion, CD4+ NKG2D+ represent a subset of highly differentiated T cells which characterizes the senescence of the immune system.
Figures




References
-
- Allez M, Tieng V, Nakazawa A, Treton X, Pacault V, Dulphy N, Caillat-Zucman S, Paul P, Gornet JM, Douay C, Ravet S, Tamouza R, Charron D, Lemann M, Mayer L, Toubert A. CD4+ NKG2D+ T cells in Crohn’s disease mediate inflammatory and cytotoxic responses through MICA interactions. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2346–2358. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almanzar G, Schwaiger S, Jenewein B, Keller M, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Wurzner R, Schonitzer D, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. Long-term cytomegalovirus infection leads to significant changes in the composition of the CD8+ T-cell repertoire, which may be the basis for an imbalance in the cytokine production profile in elderly persons. J Virol. 2005;79:3675–3683. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.6.3675-3683.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Arias R, Lopez-Vazquez A, Diaz-Pena R, Sampere A, Tricas L, Asensi V, Rodrigo L, Lopez-Larrea C. CD8dim and NKG2D expression defines related subsets of CD4+ T cells in HIV-infected patients with worse prognostic factors. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009;51:390–398. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e3181679015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
