Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells
- PMID: 21212348
- PMCID: PMC3089969
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1198687
Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells
Abstract
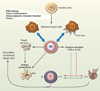
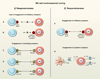
Natural killer (NK) cells were originally defined as effector lymphocytes of innate immunity endowed with constitutive cytolytic functions. More recently, a more nuanced view of NK cells has emerged. NK cells are now recognized to express a repertoire of activating and inhibitory receptors that is calibrated to ensure self-tolerance while allowing efficacy against assaults such as viral infection and tumor development. Moreover, NK cells do not react in an invariant manner but rather adapt to their environment. Finally, recent studies have unveiled that NK cells can also mount a form of antigen-specific immunologic memory. NK cells thus exert sophisticated biological functions that are attributes of both innate and adaptive immunity, blurring the functional borders between these two arms of the immune response.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA16058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI34385/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI5716/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AI51345/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA095137/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI039642/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI33903/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI039642/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA093678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI035021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA093678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA95426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68458/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI066897/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

