Measurements of neonatal bilirubin and albumin concentrations: a need for improvement and quality control
- PMID: 21213112
- PMCID: PMC3139054
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-010-1383-4
Measurements of neonatal bilirubin and albumin concentrations: a need for improvement and quality control
Abstract
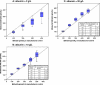
Accurate and precise bilirubin and albumin measurements are essential for proper management of jaundiced neonates. Data hereon are lacking for Dutch laboratories. We aimed to determine variability of measurements of bilirubin and albumin concentrations typical for (preterm) neonates. Aqueous, human serum albumin-based samples with different concentrations of bilirubin (100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 μmol/L) and albumin (0, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 g/L) were sent to laboratories of all Dutch neonatal intensive care units (n = 10). Bilirubin and albumin recoveries of the specimens were measured using locally available routine analytical methods. The mean, standard deviation, and coefficients of variations (CV) were calculated per sample. Bilirubin concentrations were underestimated in the absence of albumin (maximal CV 26.0%). When the albumin concentration was 10 or 20 g/L, the bilirubin concentrations of the samples were overestimated (maximal CV 14.1% and 9.2%, respectively). Variability increased with higher weighed-in bilirubin concentrations. Measured albumin levels were ~10% lower than albumin levels of manufactured samples. Bilirubin concentration did not influence albumin measurements. The maximal CV was 6.8%. In conclusion, interlaboratory variability of bilirubin and albumin measurements is high. Recalibration and introduction of a specific quality assessment scheme for neonatal samples is recommended to ensure exchangeability of bilirubin and albumin measurements among laboratories and to control the observed large variability.
Figures
References
-
- Doumas BT, Eckfeldt JH. Errors in measurement of total bilirubin: a perennial problem. Clin Chem. 1996;42:845–848. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

