Focal adhesion kinase as a cancer therapy target
- PMID: 21214510
- PMCID: PMC3267551
- DOI: 10.2174/187152010794728648
Focal adhesion kinase as a cancer therapy target
Abstract
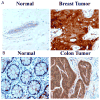
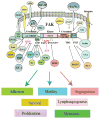
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that resides at the sites of focal adhesions. The 125 kDa FAK protein is encoded by the FAK gene located on human chromosome 8q24. Structurally, FAK consists of an amino-terminal regulatory FERM domain, a central catalytic kinase domain, and a carboxy-terminal focal adhesion targeting domain. FAK has been shown to be an important mediator of cell adhesion, growth, proliferation, survival, angiogenesis and migration, all of which are often disrupted in cancer cells. Normal tissues have low expression of FAK, while primary and metastatic tumors significantly overexpress this protein. This review summarizes expression of FAK by immunohistochemical staining in different tumor types and presents several FAK inhibition therapy approaches.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focal adhesion kinase and cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2009 Apr;24(4):503-10. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.503. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19224453 Review.
-
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK): emerging target for drug-resistant malignant tumors.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 20;52(1):248. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10296-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39976799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal adhesion kinase: a potential target in cancer therapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Mar 1;73(5):597-609. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.08.011. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 16997283 Review.
-
Evolving therapies and FAK inhibitors for the treatment of cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010 Dec;10(10):722-34. doi: 10.2174/187152010794728657. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 21291406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting focal adhesion kinase in neuroblastoma.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010 Dec;10(10):714-21. doi: 10.2174/187152010794728684. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 21269252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-target drugs: the trend of drug research and development.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040262. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768266 Free PMC article.
-
FAK and Nanog cross talk with p53 in cancer stem cells.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 May;13(4):576-80. doi: 10.2174/1871520611313040006. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 22934707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The FAK inhibitor BI 853520 exerts anti-tumor effects in breast cancer.Oncogenesis. 2018 Sep 20;7(9):73. doi: 10.1038/s41389-018-0083-1. Oncogenesis. 2018. PMID: 30237500 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging targets in cancer drug resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2019 Jun 19;2(2):161-177. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2018.27. eCollection 2019. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 35582722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential diagnostic and therapeutic target genes for lung squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):169-180. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10300. Epub 2019 May 2. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Owens LV, Xu L, Craven RJ, Dent GA, Weiner TM, Kornberg L, Liu ET, Cance WG. Overexpression of the focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) in invasive human tumors. Cancer Res. 1995;55(13):2752–2755. - PubMed
-
- Golubovskaya V, Beviglia L, Xu LH, Earp HS, 3rd, Craven R, Cance W. Dual inhibition of focal adhesion kinase and epidermal growth factor receptor pathways cooperatively induces death receptor-mediated apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(41):38978–38987. - PubMed
-
- Madan R, Smolkin MB, Cocker R, Fayyad R, Oktay MH. Focal adhesion proteins as markers of malignant transformation and prognostic indicators in breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2006;37(1):9–15. - PubMed
-
- Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD. Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18(5):516–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

