Structure/function of human killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors: lessons from polymorphisms, evolution, crystal structures and mutations
- PMID: 21214544
- PMCID: PMC3044898
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03398.x
Structure/function of human killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors: lessons from polymorphisms, evolution, crystal structures and mutations
Abstract
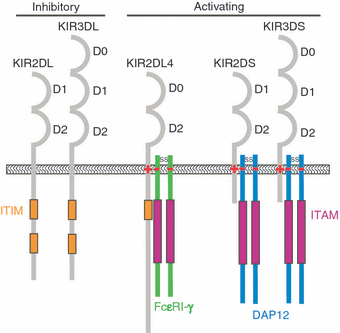
Stimulation or tolerance of natural killer (NK) cells is achieved through a cross-talk of signals derived from cell surface activating and inhibitory receptors. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) are a family of highly polymorphic activating and inhibitory receptors that serve as key regulators of human NK cell function. Distinct structural domains in different KIR family members determine function by providing docking sites for ligands or signalling proteins. Here, we review a growing body of literature that has identified important structural elements on KIR that contribute to function through studies of engineered mutants, natural polymorphic sequence variants, crystal structure data and the conservation of protein sequences throughout primate evolution. Extensive natural polymorphism is associated with both human KIR and their ligands, MHC class I (HLA-A, -B and -C) molecules, and numerous studies have demonstrated associations between inheritance of certain combinations of KIR and HLA genes and susceptibility to several diseases, including viral infections, autoimmune disorders and cancers. In addition, certain KIR/HLA combinations can influence pregnancy and the outcome of haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In view of the significant regulatory influences of KIR on immune function and human health, it is essential to fully understand the impacts of these polymorphic sequence variations on ligand recognition, expression and function of the receptor.
© 2011 The Authors. Immunology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- MacFarlane AW, IV, Campbell KS. Signal transduction in natural killer cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;298:23–57. - PubMed
-
- Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Kelly JM, et al. Activation of NK cell cytotoxicity. Mol Immunol. 2005;42:501–10. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Lanier LL. Natural killer cells and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2003;90:127–56. - PubMed
-
- Vilches C, Parham P. KIR: diverse, rapidly evolving receptors of innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:217–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

