Cyclic GMP controls Rhodospirillum centenum cyst development
- PMID: 21214648
- PMCID: PMC4273943
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07513.x
Cyclic GMP controls Rhodospirillum centenum cyst development
Abstract
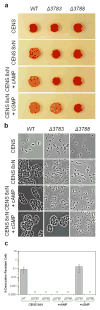
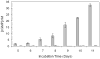
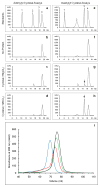
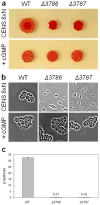
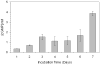
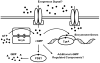
Adenylyl cyclases are widely distributed across all kingdoms whereas guanylyl cyclases are generally thought to be restricted to eukaryotes. Here we report that the α-proteobacterium Rhodospirillum centenum secretes cGMP when developing cysts and that a guanylyl cyclase deletion strain fails to synthesize cGMP and is defective in cyst formation. The R. centenum cyclase was purified and shown to effectively synthesize cGMP from GTP in vitro, demonstrating that it is a functional guanylyl cyclase. A homologue of the Escherichia coli cAMP receptor protein (CRP) is linked to the guanylyl cyclase and when deleted is deficient in cyst development. Isothermal calorimetry (ITC) and differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) analyses demonstrate that the recombinant CRP homologue preferentially binds to, and is stabilized by cGMP, but not cAMP. This study thus provides evidence that cGMP has a crucial role in regulating prokaryotic development. The involvement of cGMP in regulating bacterial development has broader implications as several plant-interacting bacteria contain a similar cyclase coupled by the observation that Azospirillum brasilense also synthesizes cGMP when inducing cysts.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Berleman JE, Bauer CE. Characterization of cyst cell formation in the purple photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum centenum. Microbiology. 2004;150:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Berleman JE, Bauer CE. Involvement of a Che-like signal transduction cascade in regulating cyst cell development in Rhodospirillum centenum. Mol Microbiol. 2005;56:1457–1466. - PubMed
-
- Bernlohr RW, Haddox MK, Goldberg ND. Cyclic guanosine 3′:5′-monophosphate in Escherichia coli and Bacillus lichenformis. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:4329–4331. - PubMed
-
- Biswas KH, Shenoy AR, Dutta A, Visweswariah SS. The evolution of guanylyl cyclases as multidomain proteins: conserved features of kinase-cyclase domain fusions. J Mol Evol. 2009;68:587–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

