Genetic engineering of trimers of hypoallergenic fragments of the major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, for allergy vaccination
- PMID: 21215346
- PMCID: PMC4092211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.12.080
Genetic engineering of trimers of hypoallergenic fragments of the major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, for allergy vaccination
Abstract
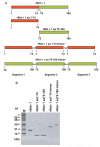
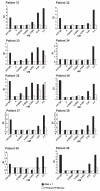
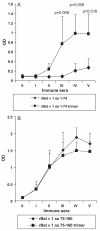
An immunotherapy trial performed in allergic patients with hypoallergenic recombinant fragments, comprising aa 1-74 and 75-160 of the major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, has indicated that the induction of allergen-specific IgG responses may be an important mechanism of this treatment. To investigate whether the immunogenicity of the rBet v 1 fragments can be increased, recombinant trimers of the fragments were produced. For this purpose, DNA trimers of rBet v 1 aa 1-74 as well as of rBet v 1 aa 75-160 were subcloned into expression plasmid pET 17b, expressed in Escherichia coli and purified. The fragments as well as the fragment trimers showed a reduced IgE-binding capacity and allergenic activity compared to rBet v 1 wildtype when tested in allergic patients. Both rBet v 1 aa 75-160 monomer and trimer induced high titers of allergen-specific IgG1 Abs in mice. Interestingly, rBet v 1 aa 1-74 trimer induced a much higher IgG(1) response to rBet v 1 than rBet v 1 aa 1-74 monomer. Consequently, IgG Abs induced with the rBet v 1 aa 1-74 trimer inhibited birch pollen allergic patients' IgE-binding 10-fold more efficiently than IgG Abs induced with the monomer. Our data show that the immunogenicity of allergy vaccines can be increased by oligomerization.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bousquet J, Lockey R, Malling HJ. Allergen immunotherapy: therapeutic vaccines for allergic diseases. A WHO position paper. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;102(4 Pt 1):558–62. - PubMed
-
- Mellerup MT, Hahn GW, Poulsen LK, Malling H. Safety of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Relation between dosage regimen, allergen extract, disease and systemic side-effects during induction treatment. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000;30(10):1423–9. - PubMed
-
- Valenta R, Ferreira F, Focke-Tejkl M, Linhart B, Niederberger V, Swoboda I, et al. From allergen genes to allergy vaccines. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010;28:211–41. - PubMed
-
- Vrtala S, Focke-Tejkl M, Swoboda I, Kraft D, Valenta R. Strategies for converting allergens into hypoallergenic vaccine candidates. Methods. 2004;32(3):313–20. - PubMed
-
- Vrtala S, Hirtenlehner K, Vangelista L, Pastore A, Eichler HG, Sperr WR, et al. Conversion of the major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, into two nonanaphylactic T cell epitope-containing fragments: candidates for a novel form of specific immunotherapy. J Clin Invest. 1997;99(7):1673–81. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

