The acridone derivative MBLI-87 sensitizes breast cancer resistance protein-expressing xenografts to irinotecan
- PMID: 21216589
- PMCID: PMC6936733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.11.019
The acridone derivative MBLI-87 sensitizes breast cancer resistance protein-expressing xenografts to irinotecan
Abstract
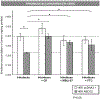
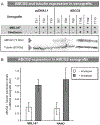
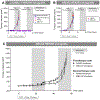
The breast cancer resistance protein ABCG2 confers cellular resistance to irinotecan (CPT-11) and its active metabolite SN-38. We utilised ABCG2-expressing xenografts as a model to evaluate the ability of a non-toxic ABCG2 inhibitor to increase intracellular drug accumulation. We assessed the activity of irinotecan in vivo in SCID mice: irinotecan completely inhibited the development of control pcDNA3.1 xenografts, whilst only delaying the growth of ABCG2-expressing xenografts. Addition of MBLI-87, an acridone derivative inhibitor, significantly increased the irinotecan effect against the growth of ABCG2-expressing xenografts. In vitro, MBLI-87 was as potent as GF120918 against ABCG2-mediated irinotecan efflux, and additionally was specific for ABCG2. A significant sensitisation to irinotecan was achieved despite the fact that doses remained well below the maximum tolerated dose (due to the rather limited solubility of MBLI-87). This suggested that MBLI-87 is an excellent candidate to prevent drug efflux by ABCG2, without altering plasma concentrations of irinotecan and SN-38 after IP (intra-peritoneal) injections. This could constitute a useful strategy to improve drug pharmacology, to facilitate drug penetration into normal tissue compartments protected by ABCG2, and potentially to reverse drug resistance in cancer cells.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Deeken JF, Figg WD, Bates SE, Sparreboom A. Toward individualized treatment: prediction of anticancer drug disposition and toxicity with pharmacogenetics. Anticancer Drugs 2007;18(2):111–26. - PubMed
-
- Polli JW, Olson KL, Chism JP, et al. An unexpected synergist role of P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein on the central nervous system penetration of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib (N-{3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorobenzyl)oxy]phenyl}−6-[5-({[2-(methylsulfonyl)ethyl]amino}methyl)-2-furyl]-4-quinazolinamine; GW572016). Drug Metab Dispos 2009;37(2):439–42. - PubMed
-
- Smith NF, Figg WD, Sparreboom A. Pharmacogenetics of irinotecan metabolism and transport: an update. Toxicol In Vitro 2006;20(2):163–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

