The spectrum of the behavioral phenotype in boys and adolescents 47,XXY (Klinefelter syndrome)
- PMID: 21217607
- PMCID: PMC3740580
The spectrum of the behavioral phenotype in boys and adolescents 47,XXY (Klinefelter syndrome)
Abstract
The behavioral phenotype of 47,XXY (Klinefelter syndrome) includes increased risks for developmental delays, language-based learning disabilities, executive dysfunction/ADHD, and socialemotional difficulties. However there is significant variability between individuals with 47,XXY, and many children and adolescents have minimal or no behavioral features while others have quite significant involvement. This paper describes behavioral features in a cohort of 57 children and adolescents with 47,XXY, including results on standardized measures of behavior (BASC-2), attention (Conner's Rating Scales), and social skills (Social Responsiveness Scale). A subset was directly assessed for autism spectrum disorders using the ADOS and ADIR. We discuss our results within the context of previous literature, including implications for genetic counseling, recommendations for care, and areas for future research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
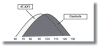
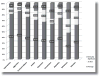




References
-
- Klinefelter H, Reifenstein E, Albright F. Syndrome characteristized by gynecomastia spermatogenes without A-leydigism, increased excretion of follicle stimulating hormone. Journal of clinical endocrine metabolism. 1942;2:615–627.
-
- Jacobs PA, Strong JA. A case of human intersexuality having a possible XXY sex-determining mechanism. Nature. 1959;183(4657):302–303. - PubMed
-
- Evans JA, de von Flindt R, Greenberg C, Ramsay S, Hamerton JL. A cytogenetic survey of 14,069 newborn infants. IV. Further follow-up on the children with sex chromosome anomalies Birth defects. Orig Artic Ser. 1982;18:169–184. - PubMed
-
- Abramsky L, Chapple J. 47,XXY (Klinefelter syndrome) 47,XYY: estimated rates of and indication for postnatal diagnosis with implications for prenatal counselling. prenat diagn. 1997;4:363–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
