The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance
- PMID: 21217695
- PMCID: PMC3076025
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2279
The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance
Abstract
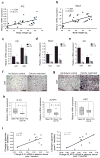
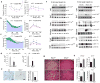
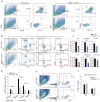
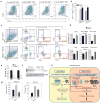
The emergence of chronic inflammation during obesity in the absence of overt infection or well-defined autoimmune processes is a puzzling phenomenon. The Nod-like receptor (NLR) family of innate immune cell sensors, such as the nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3 (Nlrp3, but also known as Nalp3 or cryopyrin) inflammasome are implicated in recognizing certain nonmicrobial originated 'danger signals' leading to caspase-1 activation and subsequent interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18 secretion. We show that calorie restriction and exercise-mediated weight loss in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes is associated with a reduction in adipose tissue expression of Nlrp3 as well as with decreased inflammation and improved insulin sensitivity. We further found that the Nlrp3 inflammasome senses lipotoxicity-associated increases in intracellular ceramide to induce caspase-1 cleavage in macrophages and adipose tissue. Ablation of Nlrp3 in mice prevents obesity-induced inflammasome activation in fat depots and liver as well as enhances insulin signaling. Furthermore, elimination of Nlrp3 in obese mice reduces IL-18 and adipose tissue interferon-γ (IFN-γ) expression, increases naive T cell numbers and reduces effector T cell numbers in adipose tissue. Collectively, these data establish that the Nlrp3 inflammasome senses obesity-associated danger signals and contributes to obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance.
Figures


Comment in
-
Linking the inflammasome to obesity-related disease.Nat Med. 2011 Feb;17(2):164-5. doi: 10.1038/nm0211-164. Nat Med. 2011. PMID: 21297609 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

