The inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases
- PMID: 21219188
- PMCID: PMC4067317
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101405
The inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases
Abstract
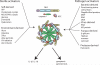
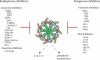
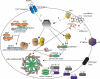
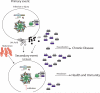
Inflammasome activation leads to caspase-1 activation, which causes the maturation and secretion of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 among other substrates. A subgroup of the NLR (nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat containing) proteins are key mediators of the inflammasome. Studies of gene-deficient mice and cells have implicated NLR inflammasomes in a host of responses to a wide range of microbial pathogens, inflammatory diseases, cancer, and metabolic and autoimmune disorders. Determining exactly how the inflammasome is activated in these diseases and disease models remains a challenge. This review presents and integrates recent progress in the field.
Figures
References
-
- Ting JP, Davis BK. CATERPILLER: a novel gene family important in immunity, cell death, and diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005;23:387–-414. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM. Are innate immune signaling pathways in plants and animals conserved? Nat. Immunol. 2005;6:973–-79. - PubMed
-
- Schroder K, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010;140:821–-32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

