The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission
- PMID: 21219302
- PMCID: PMC3058866
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02777.x
The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission
Abstract
Purpose: Focal cortical dysplasias (FCD) are localized regions of malformed cerebral cortex and are very frequently associated with epilepsy in both children and adults. A broad spectrum of histopathology has been included in the diagnosis of FCD. An ILAE task force proposes an international consensus classification system to better characterize specific clinicopathological FCD entities.
Methods: Thirty-two Task Force members have reevaluated available data on electroclinical presentation, imaging, neuropathological examination of surgical specimens as well as postsurgical outcome.
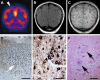
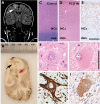
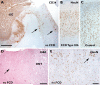
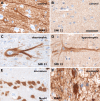
Key findings: The ILAE Task Force proposes a three-tiered classification system. FCD Type I refers to isolated lesions, which present either as radial (FCD Type Ia) or tangential (FCD Type Ib) dyslamination of the neocortex, microscopically identified in one or multiple lobes. FCD Type II is an isolated lesion characterized by cortical dyslamination and dysmorphic neurons without (Type IIa) or with balloon cells (Type IIb). Hence, the major change since a prior classification represents the introduction of FCD Type III, which occurs in combination with hippocampal sclerosis (FCD Type IIIa), or with epilepsy-associated tumors (FCD Type IIIb). FCD Type IIIc is found adjacent to vascular malformations, whereas FCD Type IIId can be diagnosed in association with epileptogenic lesions acquired in early life (i.e., traumatic injury, ischemic injury or encephalitis).
Significance: This three-tiered classification system will be an important basis to evaluate imaging, electroclinical features, and postsurgical seizure control as well as to explore underlying molecular pathomechanisms in FCD.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2010 International League Against Epilepsy.
Figures






Comment in
-
Revising the classification of focal cortical dysplasias.Epilepsia. 2011 Jan;52(1):188-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02923.x. Epilepsia. 2011. PMID: 21219307 No abstract available.
-
Commentary on the new ILAE classification system for focal cortical dysplasias.Epilepsia. 2012 Jan;53(1):219-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03321.x. Epilepsia. 2012. PMID: 22221161 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andre VM, Wu N, Yamazaki I, Nguyen ST, Fisher RS, Vinters HV, Mathern GW, Levine MS, Cepeda C. Cytomegalic interneurons: a new abnormal cell type in severe pediatric cortical dysplasia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007;66:491–504. - PubMed
-
- Andres M, Andre VM, Nguyen S, Salamon N, Cepeda C, Levine MS, Leite JP, Neder L, Vinters HV, Mathern GW. Human Cortical Dysplasia and Epilepsy: An Ontogenetic Hypothesis Based on Volumetric MRI and NeuN Neuronal Density and Size Measurements. Cereb Cortex. 2005;15:194–210. - PubMed
-
- Barkovich AJ, Kjos BO, Jackson DE, Jr., Norman D. Normal maturation of the neonatal and infant brain: MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology. 1988;166:173–180. - PubMed
-
- Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Bollen AW, Grant PE. Focal transmantle dysplasia: a specific malformation of cortical development. Neurology. 1997;49:1148–1152. - PubMed
-
- Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB. A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology. 2005;65:1873–1887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

