A reusable framework for health counseling dialogue systems based on a behavioral medicine ontology
- PMID: 21220044
- PMCID: PMC3063319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbi.2010.12.006
A reusable framework for health counseling dialogue systems based on a behavioral medicine ontology
Abstract
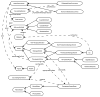
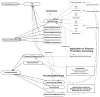
Automated approaches to promoting health behavior change, such as exercise, diet, and medication adherence promotion, have the potential for significant positive impact on society. We describe a theory-driven computational model of dialogue that simulates a human health counselor who is helping his or her clients to change via a series of conversations over time. Applications built using this model can be used to change the health behavior of patients and consumers at low cost over a wide range of media including the web and the phone. The model is implemented using an OWL ontology of health behavior change concepts and a public standard task modeling language (ANSI/CEA-2018). We demonstrate the power of modeling dialogue using an ontology and task model by showing how an exercise promotion system developed in the framework was re-purposed for diet promotion with 98% reuse of the abstract models. Evaluations of these two systems are presented, demonstrating high levels of fidelity to best practices in health behavior change counseling.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Mokdad AH, Marks JS, Stroup D, Gerberding J. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. JAMA. 2004;291:1238–45. - PubMed
-
- Services USDoHaH. Physical activity and health: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Servies, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; 1996.
-
- Bouchard C, Stephens T. Physical activity and health: international proceedings and consensus statement. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1994.
-
- Stewart A, Haskell W. Endurance exercise and health-related quality of life in 50–65 year old adults. The Gerontologist. 1993;33:782–789. - PubMed
-
- LaPorte R, Adams L, Savage D, Brenes G, Dearwater S, Cook T. The spectrum of physical activity, cardiovascular disease and health: an epidemiologic perspective. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1984;120:507–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

