Functional contributions of N- and O-glycans to L-selectin ligands in murine and human lymphoid organs
- PMID: 21224079
- PMCID: PMC3070580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.009
Functional contributions of N- and O-glycans to L-selectin ligands in murine and human lymphoid organs
Abstract
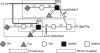
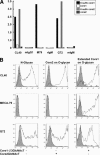
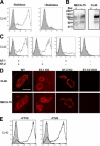
L-selectin initiates lymphocyte interactions with high endothelial venules (HEVs) of lymphoid organs through binding to ligands with specific glycosylation modifications. 6-Sulfo sLe(x), a sulfated carbohydrate determinant for L-selectin, is carried on core 2 and extended core 1 O-glycans of HEV-expressed glycoproteins. The MECA-79 monoclonal antibody recognizes sulfated extended core 1 O-glycans and partially blocks lymphocyte-HEV interactions in lymphoid organs. Recent evidence has identified the contribution of 6-sulfo sLe(x) carried on N-glycans to lymphocyte homing in mice. Here, we characterize CL40, a novel IgG monoclonal antibody. CL40 equaled or surpassed MECA-79 as a histochemical staining reagent for HEVs and HEV-like vessels in mouse and human. Using synthetic carbohydrates, we found that CL40 bound to 6-sulfo sLe(x) structures, on both core 2 and extended core 1 structures, with an absolute dependency on 6-O-sulfation. Using transfected CHO cells and gene-targeted mice, we observed that CL40 bound its epitope on both N-glycans and O-glycans. Consistent with its broader glycan-binding, CL40 was superior to MECA-79 in blocking lymphocyte-HEV interactions in both wild-type mice and mice deficient in forming O-glycans. This superiority was more marked in human, as CL40 completely blocked lymphocyte binding to tonsillar HEVs, whereas MECA-79 inhibited only 60%. These findings extend the evidence for the importance of N-glycans in lymphocyte homing in mouse and indicate that this dependency also applies to human lymphoid organs.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

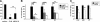
References
-
- Butcher E.C., Picker L.J. Lymphocyte homing and homeostasis. Science. 1996;272:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Vestweber D., Blanks J.E. Mechanisms that regulate the function of the selectins and their ligands. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:181–213. [Erratum appears in Physiol Rev 2000, 80: follow i] - PubMed
-
- von Andrian U.H., Mempel T.R. Homing and cellular traffic in lymph nodes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:867–878. - PubMed
-
- Miyasaka M., Tanaka T. Lymphocyte trafficking across high endothelial venules: dogmas and enigmas. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:360–370. - PubMed
-
- Rosen S.D. Ligands for L-selectin: homing, inflammation, and beyond. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:129–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

