Scaling rules for diffusive drug delivery in tumor and normal tissues
- PMID: 21224417
- PMCID: PMC3033252
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1018154108
Scaling rules for diffusive drug delivery in tumor and normal tissues
Abstract
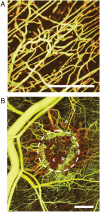
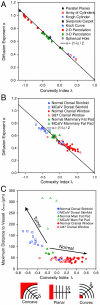
Delivery of blood-borne molecules and nanoparticles from the vasculature to cells in the tissue differs dramatically between tumor and normal tissues due to differences in their vascular architectures. Here we show that two simple measures of vascular geometry--δ(max) and λ--readily obtained from vascular images, capture these differences and link vascular structure to delivery in both tissue types. The longest time needed to bring materials to their destination scales with the square of δ(max), the maximum distance in the tissue from the nearest blood vessel, whereas λ, a measure of the shape of the spaces between vessels, determines the rate of delivery for shorter times. Our results are useful for evaluating how new therapeutic agents that inhibit or stimulate vascular growth alter the functional efficiency of the vasculature and more broadly for analysis of diffusion in irregularly shaped domains.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: R.K.J. received commercial research grants from Dyax, AstraZeneca, and MedImmune; consultant fees from AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Dyax, Astellas-Fibrogen, Regeneron, Genzyme, Morphosys, and Noxxon Pharma; and a speaker honorarium from Genzyme. R.K.J. owns stock in SynDevRx. No reagents or funding from these companies was used in these studies. There is no significant financial or other competing interest in the work.
Figures

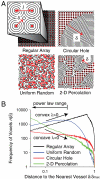
 (mean ± SEM). For comparison, published results (9) for a highly diffusible tracer (O15) in normal myocardium yielded a narrower range of transit times (hO15(t) ∼ t-3.1).
(mean ± SEM). For comparison, published results (9) for a highly diffusible tracer (O15) in normal myocardium yielded a narrower range of transit times (hO15(t) ∼ t-3.1).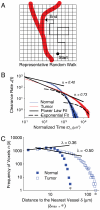
References
-
- Endrich B, Reinhold HS, Gross JF, Intaglietta M. Tissue perfusion inhomogeneity during early tumor growth in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979;62:387–395. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005;307:58–62. - PubMed
-
- West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ. A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science. 1997;276:122–126. - PubMed
-
- West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ. The fourth dimension of life: Fractal geometry and allometric scaling of organisms. Science. 1999;284:1677–1679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA073479/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA96915/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA126642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149285/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R15-CA094119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA115767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA80124/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R15 CA094119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 CA085140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R15-CA074366/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA85140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA115767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA096915/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA080124/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA126642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

