Deciphering the clinical presentations, pathogenesis, and treatment of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
- PMID: 21224460
- PMCID: PMC4047218
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2010.1977
Deciphering the clinical presentations, pathogenesis, and treatment of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
Abstract
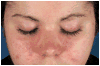
The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies or myositis syndromes (the most common forms are polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and inclusion body myositis) are systemic autoimmune diseases defined by chronic muscle weakness and inflammation of unknown etiology and result in significant morbidity and mortality. Research suggests that categorizing heterogeneous myositis syndromes into mutually exclusive and stable phenotypes by using clinical and immune response features is useful for predicting clinical signs and symptoms, associated genetic and environmental risk factors, and responses to therapy and prognosis. Knowledge of myositis phenotypes should enhance clinicians' ability to recognize and manage these rare disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Parts 1 and 2. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:344–347. 3403–407. - PubMed
-
- Oddis CV, Rider LG, Reed AM, et al. International consensus guidelines for trials of therapies in the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2607–2615. - PubMed
-
- Feldman BM, Rider LG, Reed AM, Pachman LM. Juvenile dermatomyositis and other idiopathic inflammatory myopathies of childhood. Lancet. 2008:2201–2212. - PubMed
-
- Oddis CV, Conte CG, Steen VD, Medsger TA., Jr Incidence of polymyositis-dermatomyositis: A 20-year study of hospital diagnosed cases in Allegheny County, PA 1963–1982. J Rheumatol. 1990;17:1329–1334. - PubMed
-
- Mendez EP, Lipton R, Ramsey-Goldman R, et al. US incidence of juvenile dermatomyositis, 1995–1998: results from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:300–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

