Present state and future perspectives of using pluripotent stem cells in toxicology research
- PMID: 21225242
- PMCID: PMC3026927
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-010-0641-6
Present state and future perspectives of using pluripotent stem cells in toxicology research
Abstract
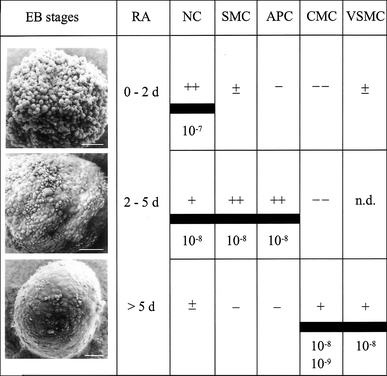
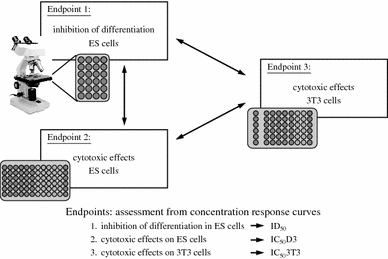
The use of novel drugs and chemicals requires reliable data on their potential toxic effects on humans. Current test systems are mainly based on animals or in vitro-cultured animal-derived cells and do not or not sufficiently mirror the situation in humans. Therefore, in vitro models based on human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) have become an attractive alternative. The article summarizes the characteristics of pluripotent stem cells, including embryonic carcinoma and embryonic germ cells, and discusses the potential of pluripotent stem cells for safety pharmacology and toxicology. Special attention is directed to the potential application of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) for the assessment of developmental toxicology as well as cardio- and hepatotoxicology. With respect to embryotoxicology, recent achievements of the embryonic stem cell test (EST) are described and current limitations as well as prospects of embryotoxicity studies using pluripotent stem cells are discussed. Furthermore, recent efforts to establish hPSC-based cell models for testing cardio- and hepatotoxicity are presented. In this context, methods for differentiation and selection of cardiac and hepatic cells from hPSCs are summarized, requirements and implications with respect to the use of these cells in safety pharmacology and toxicology are presented, and future challenges and perspectives of using hPSCs are discussed.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stem cells in toxicity testing.Arch Toxicol. 2011 Feb;85(2):77-8. doi: 10.1007/s00204-011-0650-0. Arch Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21253708 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersson H et al (2010) Assaying cardiac biomarkers for toxicity testing using biosensing and cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells. J Biotechnol 150:175–181 - PubMed
-
- Abe K, et al. Endoderm-specific gene expression in embryonic stem cells differentiated to embryoid bodies. Exp Cell Res. 1996;229:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Adler S, Lindqvist J, Uddenberg K, Hyllner J, Strehl R. Testing potential developmental toxicants with a cytotoxicity assay based on human embryonic stem cells. Altern Lab Anim. 2008;36:129–140. - PubMed
-
- Adler S, Pellizzer C, Hareng L, Hartung T, Bremer S. First steps in establishing a developmental toxicity test method based on human embryonic stem cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2008;22:200–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

