Antibacterial properties of chicken intestinal phospholipase A2
- PMID: 21226897
- PMCID: PMC3024238
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-4
Antibacterial properties of chicken intestinal phospholipase A2
Abstract
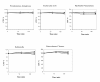
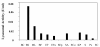
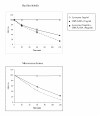
Background: The presence of chicken group-IIA PLA2 (ChPLA2-IIA) in the intestinal secretion suggests that this enzyme plays an important role in systemic bactericidal defence. We have analyzed the bactericidal activity of purified ChPLA2-IIA, on several gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria by using the diffusion well and dilution methods.
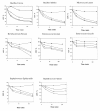
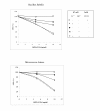
Results: ChPLA2-IIA displays potent bactericidal activity against gram-positive bacteria but lacks bactericidal activity against gram negative ones. We have also demonstrated a synergic action of ChPLA2-IIA with lysozyme when added to the bacteria culture prior to ChPLA2-IIA. The bactericidal efficiency of ChPLA2-IIA was shown to be dependent upon the presence of calcium ions and then a correlation could be made to its hydrolytic activity of membrane phospholipids. Interestingly ChPLA2-IIA displays a higher dependence to Ca²+ ions than to Mg²+ ions.
Conclusion: We conclude that the main physiological role of ChPLA2-IIA could be the defence of the intestine against bacterial invasions.
Figures
References
-
- Nevalainen TJ. Serum phospholipases A2 in inflammatory diseases. Clin Chem. 1993;39(12):2453–2459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

