Increased expression and activity of 12-lipoxygenase in oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy and proliferative diabetic retinopathy: implications in retinal neovascularization
- PMID: 21228311
- PMCID: PMC3028363
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0008
Increased expression and activity of 12-lipoxygenase in oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy and proliferative diabetic retinopathy: implications in retinal neovascularization
Erratum in
- Diabetes. 2013 Mar;62(3):998
Abstract
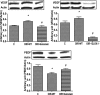
Objective: Arachidonic acid is metabolized by 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) to 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) and has an important role in the regulation of angiogenesis and endothelial cell proliferation and migration. The goal of this study was to investigate whether 12-LOX plays a role in retinal neovascularization (NV).
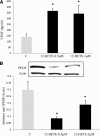
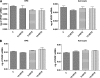
Research design and methods: Experiments were performed using retinas from a murine model of oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy (OIR) that was treated with and without the LOX pathway inhibitor, baicalein, or lacking 12-LOX. We also analyzed vitreous samples from patients with and without proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Western blotting and RT-PCR were used to assess the expression of 12-LOX, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF). Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used to assess the amounts of HETEs in the murine retina and human vitreous samples. The effects of 12-HETE on VEGF and PEDF expression were evaluated in Müller cells (rMCs), primary mouse retinal pigment epithelial cells, and astrocytes.
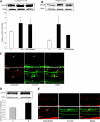
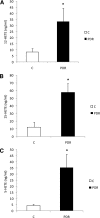
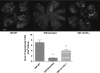
Results: Retinal NV during OIR was associated with increased 12-LOX expression and 12-, 15-, and 5-HETE production. The amounts of HETEs also were significantly higher in the vitreous of diabetic patients with PDR. Retinal NV was markedly abrogated in mice treated with baicalein or mice lacking 12-LOX. This was associated with decreased VEGF expression and restoration of PEDF levels. PEDF expression was reduced in 12-HETE-treated rMCs, astrocytes, and the retinal pigment epithelium. Only rMCs and astrocytes showed increased VEGF expression by 12-HETE.
Conclusions: 12-LOX and its product HETE are important regulators of retinal NV through modulation of VEGF and PEDF expression and could provide a new therapeutic target to prevent and treat ischemic retinopathy.
Figures
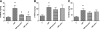
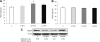
Similar articles
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits retinal microvascular dysfunction induced by 12/15-lipoxygenase-derived eicosanoids.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Mar;1851(3):290-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.12.017. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25562624 Free PMC article.
-
Vitreous levels of pigment epithelium-derived factor and vascular endothelial growth factor: implications for ocular angiogenesis.Am J Ophthalmol. 2004 Apr;137(4):668-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2003.11.015. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004. PMID: 15059706
-
Imbalanced levels of angiogenic and angiostatic factors in vitreous, plasma and postmortem retinal tissue of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.J Diabetes Complications. 2012 Sep-Oct;26(5):435-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2012.05.005. Epub 2012 Jun 12. J Diabetes Complications. 2012. PMID: 22699109
-
Key Role of 12-Lipoxygenase and Its Metabolite 12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid (12-HETE) in Diabetic Retinopathy.Curr Eye Res. 2022 Mar;47(3):329-335. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2021.1995003. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Curr Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35129022 Review.
-
Functional Roles of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor in Retinal Degenerative and Vascular Disorders: A Scoping Review.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Dec 2;65(14):41. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.14.41. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39728690 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Eicosanoids and Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Retinopathy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jun 12;9(6):520. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060520. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted knock-down of a structurally atypical zebrafish 12S-lipoxygenase leads to severe impairment of embryonic development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 20;108(51):20479-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1117094108. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22143766 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating metabolite profile in young adulthood identifies long-term diabetes susceptibility: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study.Diabetologia. 2022 Apr;65(4):657-674. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05641-x. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Diabetologia. 2022. PMID: 35041022 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of retinal neovascularization by a PEDF-derived nonapeptide in newborn mice subjected to oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Jun;195:108030. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108030. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32272114 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant soluble epoxide hydrolase and oxylipin levels in a porcine arteriovenous graft stenosis model.J Vasc Res. 2014;51(4):269-82. doi: 10.1159/000365251. Epub 2014 Sep 5. J Vasc Res. 2014. PMID: 25196102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bussolino F, Mantovani A, Persico G. Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel formation. Trends Biochem Sci 1997;22:251–256 - PubMed
-
- Miller JW, Adamis AP, Aiello LP. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular neovascularization and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Metab Rev 1997;13:37–50 - PubMed
-
- Dawson DW, Volpert OV, Gillis P, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor: a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Science 1999;285:245–248 - PubMed
-
- Murphy RC, Gijón MA. Biosynthesis and metabolism of leukotrienes. Biochem J 2007;405:379–395 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

