Structure and function of an irreversible agonist-β(2) adrenoceptor complex
- PMID: 21228876
- PMCID: PMC3074335
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09665
Structure and function of an irreversible agonist-β(2) adrenoceptor complex
Abstract
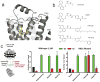
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are eukaryotic integral membrane proteins that modulate biological function by initiating cellular signalling in response to chemically diverse agonists. Despite recent progress in the structural biology of GPCRs, the molecular basis for agonist binding and allosteric modulation of these proteins is poorly understood. Structural knowledge of agonist-bound states is essential for deciphering the mechanism of receptor activation, and for structure-guided design and optimization of ligands. However, the crystallization of agonist-bound GPCRs has been hampered by modest affinities and rapid off-rates of available agonists. Using the inactive structure of the human β(2) adrenergic receptor (β(2)AR) as a guide, we designed a β(2)AR agonist that can be covalently tethered to a specific site on the receptor through a disulphide bond. The covalent β(2)AR-agonist complex forms efficiently, and is capable of activating a heterotrimeric G protein. We crystallized a covalent agonist-bound β(2)AR-T4L fusion protein in lipid bilayers through the use of the lipidic mesophase method, and determined its structure at 3.5 Å resolution. A comparison to the inactive structure and an antibody-stabilized active structure (companion paper) shows how binding events at both the extracellular and intracellular surfaces are required to stabilize an active conformation of the receptor. The structures are in agreement with long-timescale (up to 30 μs) molecular dynamics simulations showing that an agonist-bound active conformation spontaneously relaxes to an inactive-like conformation in the absence of a G protein or stabilizing antibody.
Figures
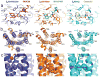

Comment in
-
Cell signalling: Binding the receptor at both ends.Nature. 2011 Jan 13;469(7329):172-3. doi: 10.1038/469172a. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21228868 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled receptors: Crystallizing how agonists bind.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Feb;10(2):97. doi: 10.1038/nrd3379. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21283100 No abstract available.
References
-
- Caffrey M. Crystallizing membrane proteins for structure determination: use of lipidic mesophases. Annu Rev Biophys. 2009;38:29–51. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Edwards PC, Burghammer M, Villa C, Schertler GF. Structure of bovine rhodopsin in a trigonal crystal form. J Mol Biol. 2004;343:1409–1438. - PubMed
-
- Palczewski K, et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 2000;289:739–745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 GM075915/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60DK-20572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM75915/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M083118/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 NS028471/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS028471/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM083118/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM075913/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM073210/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 50GM073210/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM75913/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS028471/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM56169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068603/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

