The structural basis for agonist and partial agonist action on a β(1)-adrenergic receptor
- PMID: 21228877
- PMCID: PMC3023143
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09746
The structural basis for agonist and partial agonist action on a β(1)-adrenergic receptor
Abstract
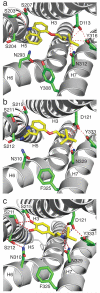
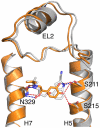
β-adrenergic receptors (βARs) are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that activate intracellular G proteins upon binding catecholamine agonist ligands such as adrenaline and noradrenaline. Synthetic ligands have been developed that either activate or inhibit βARs for the treatment of asthma, hypertension or cardiac dysfunction. These ligands are classified as either full agonists, partial agonists or antagonists, depending on whether the cellular response is similar to that of the native ligand, reduced or inhibited, respectively. However, the structural basis for these different ligand efficacies is unknown. Here we present four crystal structures of the thermostabilized turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) β(1)-adrenergic receptor (β(1)AR-m23) bound to the full agonists carmoterol and isoprenaline and the partial agonists salbutamol and dobutamine. In each case, agonist binding induces a 1 Å contraction of the catecholamine-binding pocket relative to the antagonist bound receptor. Full agonists can form hydrogen bonds with two conserved serine residues in transmembrane helix 5 (Ser(5.42) and Ser(5.46)), but partial agonists only interact with Ser(5.42) (superscripts refer to Ballesteros-Weinstein numbering). The structures provide an understanding of the pharmacological differences between different ligand classes, illuminating how GPCRs function and providing a solid foundation for the structure-based design of novel ligands with predictable efficacies.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cell signalling: Binding the receptor at both ends.Nature. 2011 Jan 13;469(7329):172-3. doi: 10.1038/469172a. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21228868 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled receptors: Crystallizing how agonists bind.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Feb;10(2):97. doi: 10.1038/nrd3379. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21283100 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H. Integrated methods for the construction of three dimensional models and computational probing of structure function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995;25:366–428.
-
- Strader CD, et al. Conserved aspartic acid residues 79 and 113 of the beta-adrenergic receptor have different roles in receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:10267–10271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

