Role of the endothelin axis and its antagonists in the treatment of cancer
- PMID: 21232046
- PMCID: PMC3087127
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01217.x
Role of the endothelin axis and its antagonists in the treatment of cancer
Abstract
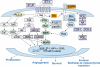
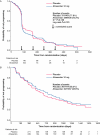
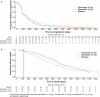
The endothelins (ET) are a group of proteins that act through G-protein coupled receptors. Endothelin-1 (ET-1) was initially identified as a potent vasoconstrictor and dysregulation of the ET axis contributes to pathological processes responsible for cardiovascular disease states. More recently, the ET axis, in particular ET-1 acting through the endothelin A receptor (ET(A) ), has been implicated in the development of several cancers through activation of pathways involved in cell proliferation, migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, osteogenesis and angiogenesis. The endothelin B receptor (ET(B) ) may counter tumour progression by promoting apoptosis and clearing ET-1; however, it has recently been implicated in the development of some tumour types including melanomas and oligodendrogliomas. Here, we review emerging preclinical and clinical data outlining the role of the ET axis in cancer, and its antagonism as an attractive and challenging approach to improve clinical cancer management. Clinical data of ET(A) antagonists in patients with prostate cancer are encouraging and provide promise for new ET(A) antagonist-based treatment strategies. Given the unexpected opportunities to affect pleiotrophic tumorigenic signals by targeting ET(A)-mediated pathways in a number of cancers, the evaluation of ET-targeted therapy in cancer warrants further investigation.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Abassi ZA, Tate JE, Golomb E, Keiser HR. Role of neutral endopeptidase in the metabolism of endothelin. Hypertension. 1992;20:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SI, Thompson J, Coulson JM, Woll PJ. Studies on the expression of endothelin, its receptor subtypes, and converting enzymes in lung cancer and in human bronchial epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000;22:422–431. - PubMed
-
- Alanen K, Deng DX, Chakrabarti S. Augmented expression of endothelin-1, endothelin-3 and the endothelin-B receptor in breast carcinoma. Histopathology. 2000;36:161–167. - PubMed
-
- Anguelova E, Beuvon F, Leonard N, Chaverot N, Varlet P, Couraud PO, et al. Functional endothelin ET B receptors are selectively expressed in human oligodendrogliomas. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;137:77–88. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong AJ, Creel P, Turnbull J, Moore C, Jaffe TA, Haley S, et al. A Phase I-II study of docetaxel and atrasentan in men with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6270–6276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

