Blood lipid profiles and peripheral blood mononuclear cell cholesterol metabolism gene expression in patients with and without methotrexate treatment
- PMID: 21232092
- PMCID: PMC3033360
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-4
Blood lipid profiles and peripheral blood mononuclear cell cholesterol metabolism gene expression in patients with and without methotrexate treatment
Abstract
Background: Methotrexate (MTX) is the most commonly prescribed disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) in rheumatoid arthritis. ATP-binding cassette transporter-A1 (ABCA1) and 27-Hydroxylase (HY27) are known antiatherogenic proteins that promote cellular cholesterol efflux. In THP-1 macrophages, MTX can promote the reversal of cholesterol transport, limit foam cell formation and also reverse COX-2 inhibitor-mediated downregulation of ABCA1. Despite its antiatherogenic potential in vitro, the impact of clinical use of low-dose MTX on cholesterol metabolism in humans is unknown. Objective of the study was to examine whether clinical MTX use is associated with altered blood lipids and/or ABCA1/HY27 expressions.
Methods: In all, 100 rheumatoid arthritis subjects were recruited from a medical center in central Taiwan. Plasma lipid profiles and peripheral blood mononuclear cell HY27 and ABCA1 expressions were compared between subjects taking MTX (MTX+) and other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) (MTX-). Dietary intake was assessed by a registered dietician.
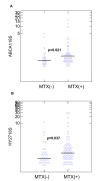
Results: Though no difference observed in the blood lipids between MTX+ and MTX- subjects, the expressions of ABCA1 and HY27 were significantly elevated in MTX+ subjects (n = 67) compared to MTX- subjects (n = 32, p < 0.05). ABCA expression correlated with MTX doses (r = 0.205, p = 0.042), and MTX+ subjects are more likely to have increased HY27 compared to MTX- subjects (OR = 2.5, p = 0.038). Prevalence of dyslipidemia and overweight, and dietary fat/cholesterol intake were lower than that of the age-matched population. Although no differences were observed in the blood lipids, the potential impacts of MTX on cholesterol metabolism should not be overlooked and the atheroprotective effects from MTX induced HY27 and ABCA1 expressions may still be present in those persons with pre-existing dyslipidemia.
Conclusions: We demonstrated novel findings on the increased gene expressions of atheroprotective protein HY27 and ABCA1 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with clinical use of low-dose MTX. Whether MTX induced HY27 and ABCA1 expressions can protect against cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic inflammation through the facilitation of cholesterol export remains to be established. Further studies on the impacts of low-dose MTX on hypercholesterolemic patients are underway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Atheroprotective effects of methotrexate on reverse cholesterol transport proteins and foam cell transformation in human THP-1 monocyte/macrophages.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Dec;58(12):3675-83. doi: 10.1002/art.24040. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 19035488 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition on cholesterol efflux proteins and atheromatous foam cell transformation in THP-1 human macrophages: a possible mechanism for increased cardiovascular risk.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(1):R4. doi: 10.1186/ar2109. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17244362 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lipid-lowering drugs on reverse cholesterol transport gene expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear and HepG2 cells.Pharmacogenomics. 2010 Sep;11(9):1235-46. doi: 10.2217/pgs.10.93. Pharmacogenomics. 2010. PMID: 20860464
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: important targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 May;12(5):647-60. doi: 10.2174/138945011795378522. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21039336 Review.
-
Lipid efflux by the ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Jul;1761(7):655-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.04.012. Epub 2006 May 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16798073 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L.) Seed and Peel Methanolic Extracts on Oxidative Stress and Lipid Profile Changes Induced by Methotrexate in Rats.Adv Pharm Bull. 2017 Jun;7(2):269-274. doi: 10.15171/apb.2017.032. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28761829 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Dietary Cholesterol on the Pathophysiology of Infectious and Autoimmune Disease.Nutrients. 2018 Jun 13;10(6):764. doi: 10.3390/nu10060764. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29899295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Drug Effects on Primary Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells Activated by Serum Amyloid A.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Feb 13;2018:8237209. doi: 10.1155/2018/8237209. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 29670468 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism and rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 May 31;14:1190607. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190607. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37325667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Closing the loop on inflammation and atherothrombosis: why perform the CIRT and CANTOS trials?Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2013;124:174-90. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2013. PMID: 23874021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ward JR. Historical perspective on the use of methotrexate for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1985;12(Suppl 12):3–6. - PubMed
-
- Tian H, Cronstein BN. Understanding the mechanisms of action of methotrexate: implications for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65:168–173. - PubMed
-
- Chih HM, Chang HY, Chen DY, Lan JL, Chiang EP. Low-dose methotrexate treatment is associated with increased total cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol in blood: a pilot study (Chinese) Nutri Sci J. in press .
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

