Endovascular stroke treatment today
- PMID: 21233233
- PMCID: PMC7965694
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2346
Endovascular stroke treatment today
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to review current treatment options in acute ischemic stroke, focusing on the latest advances in the field of mechanical recanalization. These devices recently made available for endovascular intracranial thrombectomy show great potential in acute stroke treatments. Compelling evidence of their recanalization efficacy comes from current mechanical embolectomy trials. In addition to allowing an extension of the therapeutic time window, mechanical recanalization devices can be used without adjuvant thrombolytic therapy, thus diminishing the intracranial bleeding risk. Therefore, these devices are particularly suitable in patients in whom thrombolytic therapy is contraindicated. IV and IA thrombolysis and bridging therapy are viable options in acute stroke treatment. Mechanical recanalization devices can potentially have a clinically relevant impact in the interventional treatment of stroke, but at the present time, a randomized study would be beneficial.
Figures
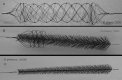
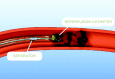

References
-
- NINDS rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1581–87 - PubMed
-
- Heuschmann PU, Berger K, Misselwitz B, et al. . Frequency of thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke and the risk of in-hospital mortality: the German Stroke Registers Study Group. Stroke 2003;34:1106–13 - PubMed
-
- Schumacher HC, Bateman BT, Boden-Albala B, et al. . Use of thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample 1999 to 2004. Ann Emerg Med 2007;50:99–107 - PubMed
-
- Weimar C, Kraywinkel K, Maschke M, et al. . Intravenous thrombolysis in German stroke units before and after regulatory approval of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Cerebrovasc Dis 2006;22:429–31 - PubMed
-
- Albers GW, Thijs VN, Wechsler L, et al. , for the DEFUSE Investigators. Magnetic resonance imaging profiles predict clinical response to early reperfusion: the Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging Evaluation for Understanding Stroke Evolution (DEFUSE) study. Ann Neurol 2006;60:508–17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
