Sex differences in lopinavir and ritonavir pharmacokinetics among HIV-infected women and men
- PMID: 21233301
- PMCID: PMC3325020
- DOI: 10.1177/0091270010388650
Sex differences in lopinavir and ritonavir pharmacokinetics among HIV-infected women and men
Abstract
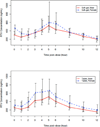
The authors compared the pharmacokinetics of lopinavir (LPV) and ritonavir (RTV) between women and men. This 2-step, multicenter, pharmacokinetic study enrolled human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected adults on lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) capsules (400/100 mg bid) plus 1 or more nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. All participants underwent 12-hour pharmacokinetic sampling. The pharmacokinetic sampling was repeated in participants receiving the LPV/r tablet formulation. Step 1 enrolled 37 women and 40 men; step 2 included 42 participants from step 1 plus 35 new participants (39 women and 38 men). LPV pharmacokinetics in women and men were not significantly different with either formulation. Women had significantly higher median RTV AUC(0-12 h) with both the soft-gel capsule (SGC) and tablet formulations (SGC: 5395 vs 4119 ng·h/mL, P = .026; tablet: 5310 vs 3941 ng·h/mL, P = .012), higher median C(max) (SGC: 802 vs 635 ng/mL, P = .032; tablet: 773 vs 570 ng/mL, P = .006), and lower median CL/F (SGC: 18.54 vs 24.31 L/h, P = .026; tablet: 18.83 vs 25.37 L/h, P = .012). RTV CL/F was slower in women after weight adjustment with both formulations. The pharmacokinetics of LPV in the SGC and tablet formulations are comparable in HIV-infected patients. Women had higher RTV AUC(0-12 h) and lower CL/F with both formulations. The mechanism of the sex difference in RTV CL/F warrants elucidation.
Figures
References
-
- [Accessed March 29, 2010]; JC1700_Epi_Update_2009_en.pdf. Available at http://data.unaids.org/pub/EpiReport/2009/2009.
-
- Anderson PL, Kakuda TN, Kawle S, Fletcher CV. Antiviral dynamics and sex differences of zidovudine and lamivudine triphosphate concentrations in HIV-infected individuals. AIDS. 2003;17(15):2159–2168. - PubMed
-
- Bersoff-Matcha SJ, Miller WC, Aberg JA, van Der Horst C, Hamrick HJ, Jr, Powderly WG, Mundy LM. Sex differences in nevirapine rash. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(1):124–129. Epub 2000 Dec 13. - PubMed
-
- Burger DM, van der Heiden I, La Porte CJL, van er Ende ME, Groeneveld P, Richter C, Koopmans PP, et al. Interpatient variability in the pharmacokinetics of the HIV non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor: efavirenz: the effect of gender, age, race, and CYP2B6 polymorphism. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;61(2):148–154. 2003. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van de Leur MR, Burger DM, La Porte CJ, Koopmans PP. A retrospective TDM database analysis of interpatient variability in the pharmacokinetics of lopinavir in HIV-infected adults. Ther Drug Monit. 2006 Oct;28(5):650–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI056933/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069450/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI-38858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069411/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI 56933/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000034/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI-68634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069465/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069411/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UOI AI 069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069556/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000044/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046370/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025915/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069415/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UOI AI68636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069556/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069465/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical