Health advocacy organizations and the pharmaceutical industry: an analysis of disclosure practices
- PMID: 21233424
- PMCID: PMC3052325
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2010.300027
Health advocacy organizations and the pharmaceutical industry: an analysis of disclosure practices
Abstract
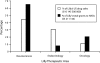
Health advocacy organizations (HAOs) are influential stakeholders in health policy. Although their advocacy tends to closely correspond with the pharmaceutical industry's marketing aims, the financial relationships between HAOs and the pharmaceutical industry have rarely been analyzed. We used Eli Lilly and Company's grant registry to examine its grant-giving policies. We also examined HAO Web sites to determine their grant-disclosure patterns. Only 25% of HAOs that received Lilly grants acknowledged Lilly's contributions on their Web sites, and only 10% acknowledged Lilly as a grant event sponsor. No HAO disclosed the exact amount of a Lilly grant. As highly trusted organizations, HAOs should disclose all corporate grants, including the purpose and the amount. Absent this disclosure, legislators, regulators, and the public cannot evaluate possible conflicts of interest or biases in HAO advocacy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Patient advocacy organizations and corporate relationships.Am J Public Health. 2011 Apr;101(4):582-3; author reply 583. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300087. Am J Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21389285 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Markman M. The increasingly complex world of cancer patient advocacy organizations. Curr Oncol Rep. 2008;10(1):1–2 - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Web site. Available at: http://www.diabetes.org. Accessed April 27, 2010.
-
- Batt S. Marching to different drummers: health advocacy groups in Canada and funding from the pharmaceutical industry. Available at: http://www.whp-apsf.ca/pdf/corpFunding.pdf. Published January 2005. Accessed January 4, 2011
-
- O'Donovan O. Corporate colonization of health activism? Irish health advocacy organizations' modes of engagement with pharmaceutical corporations. Int J Health Serv. 2007;37(4):711–733 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials