Creating a long-term diabetic rabbit model
- PMID: 21234414
- PMCID: PMC3014707
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/289614
Creating a long-term diabetic rabbit model
Abstract
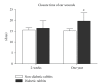
This study was to create a long-term rabbit model of diabetes mellitus for medical studies of up to one year or longer and to evaluate the effects of chronic hyperglycemia on damage of major organs. A single dose of alloxan monohydrate (100 mg/kg) was given intravenously to 20 young New Zealand White rabbits. Another 12 age-matched normal rabbits were used as controls. Hyperglycemia developed within 48 hours after treatment with alloxan. Insulin was given daily after diabetes developed. All animals gained some body weight, but the gain was much less than the age-matched nondiabetic rabbits. Hyperlipidemia, higher blood urea nitrogen and creatinine were found in the diabetic animals. Histologically, the pancreas showed marked beta cell damage. The kidneys showed significantly thickened afferent glomerular arterioles with narrowed lumens along with glomerular atrophy. Lipid accumulation in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes appeared as vacuoles. Full-thickness skin wound healing was delayed. In summary, with careful management, alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits can be maintained for one year or longer in reasonably good health for diabetic studies.
Figures

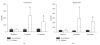


References
-
- American Diabetic Association. National Diabetes Statistics Fact Sheet. 2008. http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov/dm/pubs/statistics/index.htm.
-
- American-Diabetes-Association. All about Diabetes. 2007, http://www.diabetes.org/about-diabetes.jsp.
-
- Tesch GH, Allen TJ. Rodent models of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy (methods in renal research) Nephrology. 2007;12(3):261–266. - PubMed
-
- Lenzen S. The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia. 2008;51(2):216–226. - PubMed
-
- Rees DA, Alcolado JC. Animal models of diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Medicine. 2005;22(4):359–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
