Mechanisms of drug resistance in kinases
- PMID: 21235428
- PMCID: PMC3095104
- DOI: 10.1517/13543784.2011.546344
Mechanisms of drug resistance in kinases
Abstract
Introduction: because of their important roles in disease and excellent 'druggability', kinases have become the second largest drug target family. The great success of the BCR-ABL inhibitor imatinib in treating chronic myelogenous leukemia illustrates the high potential of kinase inhibitor (KI) therapeutics, but also unveils a major limitation: the development of drug resistance. This is a significant concern as KIs reach large patient populations for an expanding array of indications.
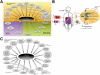
Areas covered: we provide an up-to-date understanding of the mechanisms through which KIs function and through which cells can become KI-resistant. We review current and future approaches to overcome KI resistance, focusing on currently approved KIs and KIs in clinical trials. We then discuss approaches to improve KI efficacy and overcome drug resistance and novel approaches to develop less drug resistance-prone KI therapeutics.
Expert opinion: although drug resistance is a concern for current KI therapeutics, recent progress in our understanding of the underlying mechanisms and promising technological advances may overcome this limitation and provide powerful new therapeutics.
Figures

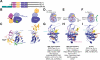


References
-
- Johnson LN. Protein kinase inhibitors: contributions from structure to clinical compounds. Q Rev Biophys. 2009 Feb;42(1):1–40. - PubMed
-
- Greenman C, Stephens P, Smith R, Dalgliesh GL, Hunter C, Bignell G, et al. Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer genomes. Nature. 2007 Mar 8;446(7132):153–8. [References 2 and 3 identified multiple mutations in kinase genes that are associated with diseases, providing a strong rationale for pursuing kinases as therapeutic targets for many indications.] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lahiry P, Torkamani A, Schork NJ, Hegele RA. Kinase mutations in human disease: interpreting genotype-phenotype relationships. Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Jan;11(1):60–74. - PubMed
-
- Quintas-Cardama A, Kantarjian H, Cortes J. Imatinib and beyond--exploring the full potential of targeted therapy for CML. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009 Sep;6(9):535–43. - PubMed
-
- Trowe T, Boukouvala S, Calkins K, Cutler RE, Jr., Fong R, Funke R, et al. EXEL-7647 inhibits mutant forms of ErbB2 associated with lapatinib resistance and neoplastic transformation. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Apr 15;14(8):2465–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
