Induction and function of virus-specific CD4+ T cell responses
- PMID: 21236461
- PMCID: PMC3082365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.12.015
Induction and function of virus-specific CD4+ T cell responses
Abstract
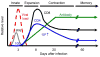
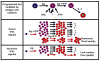
CD4+ T cells - often referred to as T-helper cells - play a central role in immune defense and pathogenesis. Virus infections and vaccines stimulate and expand populations of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in mice and in man. These virus-specific CD4+ T cells are extremely important in antiviral protection: deficiencies in CD4+ T cells are associated with virus reactivation, generalized susceptibility to opportunistic infections, and poor vaccine efficacy. As described below, CD4+ T cells influence effector and memory CD8+ T cell responses, humoral immunity, and the antimicrobial activity of macrophages and are involved in recruiting cells to sites of infection. This review summarizes a few key points about the dynamics of the CD4+ T cell response to virus infection, the positive role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the differentiation of virus-specific CD4+ T cells, and new areas of investigation to improve vaccines against virus infection.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Agnellini P, Wiesel M, Schwarz K, Wolint P, Bachmann MF, Oxenius A. Kinetic and mechanistic requirements for helping CD8 T cells. J Immunol. 2008;180(3):1517–25. - PubMed
-
- Appay V, Zaunders JJ, Papagno L, Sutton J, Jaramillo A, Waters A, Easterbrook P, Grey P, Smith D, McMichael AJ, Cooper DA, Rowland-Jones SL, Kelleher AD. Characterization of CD4(+) CTLs ex vivo. J Immunol. 2002;168(11):5954–8. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac VP, Porter BB, Harty JT. CD8+ T cell contraction is controlled by early inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(8):809–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

