Human TH17 cells express a functional IL-13 receptor and IL-13 attenuates IL-17A production
- PMID: 21236478
- PMCID: PMC3916096
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.11.043
Human TH17 cells express a functional IL-13 receptor and IL-13 attenuates IL-17A production
Abstract
Background: IL-13 is a central mediator of airway responsiveness and mucus expression in patients with allergic airway inflammation, and IL-13 is currently a therapeutic target for asthma. However, little is known about how IL-13 regulates human CD4(+) T-cell lineages because IL-13 receptor (IL-13R) α1, a subunit of IL-13R, has not previously been reported to exist on human T cells.
Objective: We sought to determine whether human CD4(+) T(H)17 cells express IL-13Rα1 and whether IL-13 regulates T(H)17 cytokine production.
Methods: Naive human CD4(+) cells were isolated from whole blood, activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28, and polarized to T(H)1, T(H)2, T(H)17, or induced regulatory T cells in the presence of IL-13 (0-10 ng/mL). Cell supernatants, total RNA, or total protein was examined 4 days after T(H)17 polarization.
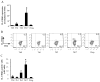
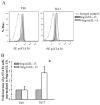
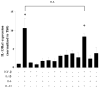
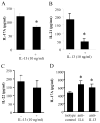
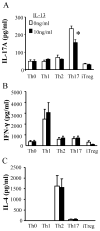
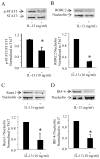
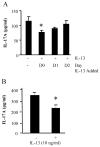
Results: T(H)17 cells, but not T(H)0, T(H)1, T(H)2, or induced regulatory T cells, expressed IL-13Rα1. IL-13 attenuated IL-17A production, as well as expression of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor, runt-related transcription factor-1, and interferon regulatory factor 4 in T(H)17-polarized cells. IL-13 neither inhibited IFN-γ production from T(H)1 cells nor inhibited IL-4 production from T(H)2 cells. Furthermore, attenuation of IL-17A production only occurred when IL-13 was present within 24 hours of T-cell activation or at the time of restimulation.
Conclusions: IL-13Rα1 is expressed on human CD4(+) T(H)17 cells, and IL-13 attenuates IL-17A production at polarization and restimulation. Although IL-13 is an attractive therapeutic target for decreasing symptoms associated with asthma, these results suggest that therapies inhibiting IL-13 production could have adverse side effects by increasing IL-17A production.
Copyright © 2011 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:
The authors have no competing interests with this study.
Figures
References
-
- Hershey GK. IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: an evolving web. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111(4):677–90. - PubMed
-
- Wills-Karp M, Luyimbazi J, Xu X, Schofield B, Neben TY, Karp CL, et al. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science. 1998;282(5397):2258–61. - PubMed
-
- Bree A, Schlerman FJ, Wadanoli M, Tchistiakova L, Marquette K, Tan XY, et al. IL-13 blockade reduces lung inflammation after Ascaris suum challenge in cynomolgus monkeys. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(5):1251–7. - PubMed
-
- Kumar RK, Herbert C, Webb DC, Li L, Foster PS. Effects of anticytokine therapy in a mouse model of chronic asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(10):1043–8. - PubMed
-
- Yang G, Volk A, Petley T, Emmell E, Giles-Komar J, Shang X, et al. Anti-IL-13 monoclonal antibody inhibits airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation and airway remodeling. Cytokine. 2004;28(6):224–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 090664/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059108/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI 070672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL106446/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI095227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI076411/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56AI076411/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090664/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL091653/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000624/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 AI 059108/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

