[Evaluation and control of hypertensive diabetics seen in Primary Care centres in Spain. BRAND II study]
- PMID: 21237535
- PMCID: PMC7025009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aprim.2010.05.016
[Evaluation and control of hypertensive diabetics seen in Primary Care centres in Spain. BRAND II study]
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to verify the level of blood pressure and glucose control and treatment in hypertensive diabetics seen in Primary Care Centres in Spain.
Design: Descriptive study conducted on hypertensive diabetic patients who attended primary care centres for any reason.
Location: Primary Care centres throughout Spain.
Participants: The study included 6,777 patients.
Measurements: Blood pressure, weight, height, waist circumference, blood analysis and treatment were recorded
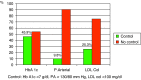
Results: The mean age of the sample was 64.40 (11.50) years. Mean blood glucose was 141.8 (39) mg/dl, glycosylated haemoglobin was ≤7% in 45.9% of the sample, and blood pressure was under control (BP≤130/80 mmHg) in 9.8% of the patients studied. LDL Cholesterol was ≤100mg/dl in 25.3% of the sample. The drugs most used to control diabetes were; sulphonylureas 2259 patients (33.3%) and biguanides 3768 patients (55.6%). A total of 556 patients were on treatment with insulin, which represented 8.2% of the population studied. The drugs most used for hypertension were; diuretics in 3395 patients (50.1%) and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in 4053 patients (59.8%).
Conclusions: A large proportion of hypertensive diabetics are insufficiently controlled.
Objetivo: Estudiar el grado de control y el tratamiento empleado en los hipertensos diabéticos atendidos en los centros de Atención Primaria en España.
Diseño: Estudio descriptivo realizado a pacientes hipertensos y diabéticos que acuden a consulta médica de Atención Primaria por cualquier motivo.
Emplazamiento: Centros de Atención Primaria de todo el territorio nacional.
Participantes: Se incluyeron 6.777 pacientes.
Mediciones principales: Se les determinó la presión arterial, peso, talla, perímetro de cintura, analítica completa y tratamiento.
Resultados: La edad media de la muestra fue de 64,40 ± 11,50 años. La glucosa media fue de 141,8 ± 39 mg/dl, la hemoglobina glicosilada fue < 7% en el 45,9% de la muestra y la presión arterial estaba controlada (PA < 130/80 mmHg) en el 9,8% de los pacientes estudiados. El LDL colesterol era inferior a 100 mg/dl en el 25,3% de los pacientes. Los fármacos más utilizados para el control de la diabetes fueron las sulfonilureas en 2.259 pacientes (33,1%) y las biguanidas en 3.768 pacientes (55,6%). Estaban en tratamiento con insulina 556 pacientes, lo que representa el 8,2%. Respecto a la hipertensión arterial los fármacos más utilizados fueron los diuréticos en 3.395 pacientes (50,1%) y los inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina en 4.053 pacientes (59,8%).
Conclusiones: Gran parte de los hipertensos diabéticos están insuficientemente controlados.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier España, S.L. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Arauz-Pacheco C., Parrot M.A., Raskin P. The treatment of hypertension in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:134–147. - PubMed
-
- Parving H.H. Controlling hypertension in diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2002;39(Suppl 2):S35–S40. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez A., Banegas J., de Andrés B., del Rey J. Principios de prevención cardiovascular. Med Clin (Barc). 1999;112:459–464. - PubMed
-
- Julius S., Majahalme S., Palatini P. Antihypertensive treatment of patients with diabetes and hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14:310S–316S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical