Inhibition of IgE-mediated secretion from human basophils with a highly selective Bruton's tyrosine kinase, Btk, inhibitor
- PMID: 21238622
- PMCID: PMC3345890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.12.018
Inhibition of IgE-mediated secretion from human basophils with a highly selective Bruton's tyrosine kinase, Btk, inhibitor
Abstract
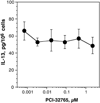
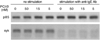
The study of receptor-mediated signaling in human basophils is often limited by the availability of selective pharmacological agents. The early signaling reaction mediated by FcεRI aggregation is thought to require the activity of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (btk), an enzyme that has been identified as important in B cells signaling because mutations lead to X-linked agammaglobulinemia. This study uses the btk selective irreversible inhibitor, PCI-32765, to explore the role of btk in a variety of functions associated with the activation of human basophils. Nine endpoints of basophil activation were examined: induced cell surface expression of CD63, CD203c, CD11b; induced secretion of histamine, LTC4, IL-4 and IL-13; the cytosolic calcium response; and the induced loss of syk kinase. Four stimuli were examined; anti-IgE antibody, formyl-met-leu-phe (FMLP), C5a and IL-3. For stimulation with anti-IgE, PCI-32765 inhibited CD63, histamine, LTC4 and IL-4 secretion with an IC50 of 3-6 nM (with 100% inhibition at 50 nM) and it inhibited CD203c and CD11b and the cytosolic calcium response with and IC50 of 30-40 nM. Fifty percent occupancy of btk with PCI-32765 occurred at ~10nM. Consistent with btk functioning downstream or in parallel to syk activation, PCI-32765 did not inhibit the loss of syk induced by anti-IgE in overnight cultures. Finally, PCI-32765 did not significantly inhibit basophil activation by FMLP or C5a and did not inhibit IL-13 release induced by IL-3. These results suggest that btk is specifically required for IgE-mediated activation of human basophils.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
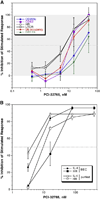
 ), CD203c (
), CD203c ( ), or CD11b (
), or CD11b ( ). The results were calculated from the net mean fluorescence intensity (above non -stimulated controls). A portion of the supernatants were analyzed for histamine (○) or LTC4 (□) by automated flourometry or radioimmunoassay, respectively. Histamine release following challenge with anti-IgE in the presence of vehicle control (0.0005% DMSO) averaged 45±17% and LTC4 release averaged 57±3 ng/µg histamine. In parallel, btk occupancy by the inhibitor was analyzed by a fluorescent probe assay (
). The results were calculated from the net mean fluorescence intensity (above non -stimulated controls). A portion of the supernatants were analyzed for histamine (○) or LTC4 (□) by automated flourometry or radioimmunoassay, respectively. Histamine release following challenge with anti-IgE in the presence of vehicle control (0.0005% DMSO) averaged 45±17% and LTC4 release averaged 57±3 ng/µg histamine. In parallel, btk occupancy by the inhibitor was analyzed by a fluorescent probe assay ( )(n=2). Panel B: IL-4 and histamine secretion in basophil-enriched (filled symbols) and purified basophil (open symbols) suspensions. Cells were incubated in media for 4 hours and stimulated with 20 ng/ml anti-IgE to optimize IL-4 secretion. Values are the mean±SEM of 3 experiments for the basophil enriched suspensions and 2 experiments (mean±range) for purified suspensions. Histamine release following challenge with anti-IgE in the presence of vehicle control (a maximum of 0.004% DMSO) from enriched suspensions (■) averaged 50±12% and IL-4 secretion (●) in enriched suspensions averaged 215±67 pg/106 basophils, similarly histamine release (□) in purified suspensions averaged 35±4% and control IL-4 secretion (○) in purified suspensions averaged 31±2 pg/106 basophils.
)(n=2). Panel B: IL-4 and histamine secretion in basophil-enriched (filled symbols) and purified basophil (open symbols) suspensions. Cells were incubated in media for 4 hours and stimulated with 20 ng/ml anti-IgE to optimize IL-4 secretion. Values are the mean±SEM of 3 experiments for the basophil enriched suspensions and 2 experiments (mean±range) for purified suspensions. Histamine release following challenge with anti-IgE in the presence of vehicle control (a maximum of 0.004% DMSO) from enriched suspensions (■) averaged 50±12% and IL-4 secretion (●) in enriched suspensions averaged 215±67 pg/106 basophils, similarly histamine release (□) in purified suspensions averaged 35±4% and control IL-4 secretion (○) in purified suspensions averaged 31±2 pg/106 basophils.

References
-
- MacGlashan DW, Jr, Vilarino N. Nonspecific Desensitization, Functional Memory and the Characteristics of SHIP Phosphorylation Following IgE-Mediated Stimulation of Human Basophils. J Immunol. 2006;177:1040–1051. - PubMed
-
- Knol EF, Koenderman L, Mul E, Verhoeven AJ, Roos D. Differential mechanisms in the stimulus-secretion coupling in human basophils: evidence for a protein-kinase-C-dependent and a protein-kinase-C-independent route. Agents Actions. 1990;30:49–52. - PubMed
-
- Miura K, MacGlashan DW., Jr Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase regulates p21ras activation during IgE-mediated stimulation of human basophils. Blood. 2000;96:2199–2205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

