Recruitment and activation of a lipid kinase by hepatitis C virus NS5A is essential for integrity of the membranous replication compartment
- PMID: 21238945
- PMCID: PMC3433060
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.12.002
Recruitment and activation of a lipid kinase by hepatitis C virus NS5A is essential for integrity of the membranous replication compartment
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a major causative agent of chronic liver disease in humans. To gain insight into host factor requirements for HCV replication, we performed a siRNA screen of the human kinome and identified 13 different kinases, including phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase III alpha (PI4KIIIα), as being required for HCV replication. Consistent with elevated levels of the PI4KIIIα product phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) detected in HCV-infected cultured hepatocytes and liver tissue from chronic hepatitis C patients, the enzymatic activity of PI4KIIIα was critical for HCV replication. Viral nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) was found to interact with PI4KIIIα and stimulate its kinase activity. The absence of PI4KIIIα activity induced a dramatic change in the ultrastructural morphology of the membranous HCV replication complex. Our analysis suggests that the direct activation of a lipid kinase by HCV NS5A contributes critically to the integrity of the membranous viral replication complex.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
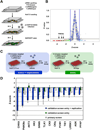

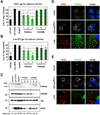
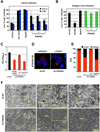

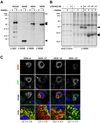
Comment in
-
Understanding how hepatitis C virus builds its unctuous home.Cell Host Microbe. 2011 Jan 20;9(1):1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.01.002. Cell Host Microbe. 2011. PMID: 21238940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balla A, Balla T. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases: old enzymes with emerging functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:351–361. - PubMed
-
- Balla T, Downing GJ, Jaffe H, Kim S, Zolyomi A, Catt KJ. Isolation and molecular cloning of wortmannin-sensitive bovine type III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:18358–18366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

