Arfaptins are localized to the trans-Golgi by interaction with Arl1, but not Arfs
- PMID: 21239483
- PMCID: PMC3064211
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.201442
Arfaptins are localized to the trans-Golgi by interaction with Arl1, but not Arfs
Abstract
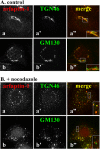
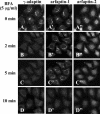
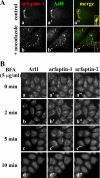
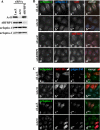
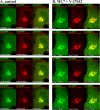
Arfaptins (arfaptin-1 and arfaptin-2/POR1) were originally identified as binding partners of the Arf small GTPases. Both proteins contain a BAR (Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs) domain, which participates in membrane deformation. Here we show that arfaptins associate with trans-Golgi membranes. Unexpectedly, Arl1 (Arf-like 1), but not Arfs, determines the trans-Golgi association of arfaptins. We also demonstrate that arfaptins interact with Arl1 through their BAR domain-containing region and compete for Arl1 binding with golgin-97 and golgin-245/p230, both of which also bind to Arl1 through their GRIP (golgin-97/RanBP2/Imh1p/p230) domains. However, arfaptins and these golgins show only limited colocalization at the trans-Golgi. Time-lapse imaging of cells overexpressing fluorescent protein-tagged arfaptins and golgin-97 reveals that arfaptins, but not golgin-97, are included in vesicular and tubular structures emanating from the Golgi region. These observations indicate that arfaptins are recruited onto trans-Golgi membranes by interacting with Arl1, and capable of inducing membrane deformation via their BAR domains.
Figures

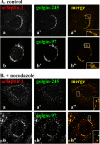
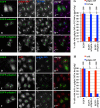
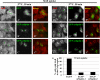
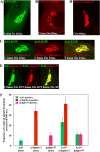
References
-
- Moss J., Vaughan M. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, 12327–12330 - PubMed
-
- D'Souza-Schorey C., Chavrier P. (2006) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 347–358 - PubMed
-
- Gillingham A. K., Munro S. (2007) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 579–611 - PubMed
-
- Kanoh H., Williger B. T., Exton J. H. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 5421–5429 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

