Lamotrigine adjunctive therapy to lithium and divalproex in depressed patients with rapid cycling bipolar disorder and a recent substance use disorder: a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study
- PMID: 21240149
- PMCID: PMC3442254
Lamotrigine adjunctive therapy to lithium and divalproex in depressed patients with rapid cycling bipolar disorder and a recent substance use disorder: a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study
Abstract
Objective: To pilot the efficacy and safety data of lamotrigine adjunctive therapy to lithium and divalproex in patients with rapid-cycling bipolar disorder (RCBD) and a recent substance use disorder (SUD).
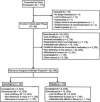
Method: Structured clinical interviews were used to ascertain DSM-IV diagnosis of RCBD, SUDs, and other Axis I disorders. Patients who did not meet the criteria for a bimodal response after up to 16-weeks of open-label treatment with lithium plus divalproex, as measured by MADRS (Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale) ≤ 19, YMRS ( Young Mania Rating Scale) ≤ 12 and GAF (Global Assessment of Functioning) = 51 for 4 weeks, were randomized to a 12- week, double-blind addition of lamotrigine or placebo to lithium plus divalproex. Primary and secondary outcomes were analyzed with ANCOVA, t-test, or chi-square/Fisher's exact.
Results: Of 98 patients enrolled into the study, 36 were randomized to receive lamotrigine (n = 18) or placebo (n ± 18), and 8 patients per arm completed the study. No patient discontinued due to adverse events. The change in MADRS total score from baseline to endpoint was -9.1 ± 11.2 in lamotrigine-treated patients versus -4.5 ± 13.1 in placebo-treated patients (p = 0.27). There were no significant differences in changes in YMRS total scores and rates of response or remission.
Conclusions: Lamotrigine adjunctive therapy was well tolerated in patients previously non-responsive to initial treatment of lithium plus divalproex. A larger study is warranted to determine the efficacy and safety of adjunctive lamotrigine versus placebo in RCBD with a recent SUD.
Figures
References
-
- Kupka RW, Luckenbaugh DA, Post RM, et al. Rapid and non-rpid cyding bipolar disorder. a meta-analysis of clinical studies. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64:1483–1494. - PubMed
-
- Schneck CD, Miklowitz DJ, Calabrese JR, et al. Phenomenology of rpid-cycling bipolar disorder: data from the first 500 participants in the Systematic Treatment Enhancement Program. Am Psychiatry. 2004;161:1902–1908. - PubMed
-
- Schneck CD. Treatment of rapid-cycling bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(Suppl. 11):22–27. - PubMed
-
- Kupka RW, Luckenbaugh DA, Post RM, et al. Comparison of rapid-cycling and non-rapid-cyding bipolar disorder based on prospective mood ratings in 539 outpatients. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162:1273–1280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical