The blockade of the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 and fatty acid amide hydrolase decreases symptoms and central sequelae in the medial prefrontal cortex of neuropathic rats
- PMID: 21241462
- PMCID: PMC3031241
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-7
The blockade of the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 and fatty acid amide hydrolase decreases symptoms and central sequelae in the medial prefrontal cortex of neuropathic rats
Abstract
Background: Neuropathic pain is a chronic disease resulting from dysfunction within the "pain matrix". The basolateral amygdala (BLA) can modulate cortical functions and interactions between this structure and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) are important for integrating emotionally salient information. In this study, we have investigated the involvement of the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) and the catabolic enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) in the morphofunctional changes occurring in the pre-limbic/infra-limbic (PL/IL) cortex in neuropathic rats.
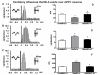
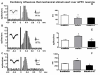
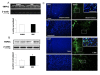
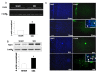
Results: The effect of N-arachidonoyl-serotonin (AA-5-HT), a hybrid FAAH inhibitor and TPRV1 channel antagonist, was tested on nociceptive behaviour associated with neuropathic pain as well as on some phenotypic changes occurring on PL/IL cortex pyramidal neurons. Those neurons were identified as belonging to the BLA-mPFC pathway by electrical stimulation of the BLA followed by hind-paw pressoceptive stimulus application. Changes in their spontaneous and evoked activity were studied in sham or spared nerve injury (SNI) rats before or after repeated treatment with AA-5-HT. Consistently with the SNI-induced changes in PL/IL cortex neurons which underwent profound phenotypic reorganization, suggesting a profound imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory responses in the mPFC neurons, we found an increase in extracellular glutamate levels, as well as the up-regulation of FAAH and TRPV1 in the PL/IL cortex of SNI rats. Daily treatment with AA-5-HT restored cortical neuronal activity, normalizing the electrophysiological changes associated with the peripheral injury of the sciatic nerve. Finally, a single acute intra-PL/IL cortex microinjection of AA-5-HT transiently decreased allodynia more effectively than URB597 or I-RTX, a selective FAAH inhibitor or a TRPV1 blocker, respectively.
Conclusion: These data suggest a possible involvement of endovanilloids in the cortical plastic changes associated with peripheral nerve injury and indicate that therapies able to normalize endovanilloid transmission may prove useful in ameliorating the symptoms and central sequelae associated with neuropathic pain.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

