Hedgehog overexpression leads to the formation of prostate cancer stem cells with metastatic property irrespective of androgen receptor expression in the mouse model
- PMID: 21241512
- PMCID: PMC3025942
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-18-6
Hedgehog overexpression leads to the formation of prostate cancer stem cells with metastatic property irrespective of androgen receptor expression in the mouse model
Abstract
Background: Hedgehog signalling has been implicated in prostate tumorigenesis in human subjects and mouse models, but its effects on transforming normal basal/stem cells toward malignant cancer stem cells remain poorly understood.
Methods: We produced pCX-shh-IG mice that overexpress Hedgehog protein persistently in adult prostates, allowing for elucidation of the mechanism during prostate cancer initiation and progression. Various markers were used to characterize and confirm the transformation of normal prostate basal/stem cells into malignant cancer stem cells under the influence of Hedgehog overexpression.
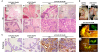
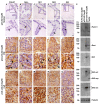
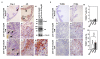
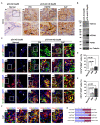
Results: The pCX-shh-IG mice developed prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) that led to invasive and metastatic prostate cancers within 90 days. The prostate cancer was initiated through activation of P63+ basal/stem cells along with simultaneous activation of Hedgehog signalling members, suggesting that P63+/Patch1+ and P63+/Smo+ cells may serve as cancer-initiating cells and progress into malignant prostate cancer stem cells (PCSCs). In the hyperplastic lesions and tumors, the progeny of PCSCs differentiated into cells of basal-intermediate and intermediate-luminal characteristics, whereas rare ChgA+ neuroendocrine differentiation was seen. Furthermore, in the metastatic loci within lymph nodes, kidneys, and lungs, the P63+ PCSCs formed prostate-like glandular structures, characteristic of the primitive structures during early prostate development. Besides, androgen receptor (AR) expression was detected heterogeneously during tumor progression. The existence of P63+/AR-, CK14+/AR- and CD44+/AR- progeny indicates direct procurement of AR- malignant cancer trait.
Conclusions: These data support a cancer stem cell scenario in which Hedgehog signalling plays important roles in transforming normal prostate basal/stem cells into PCSCs and in the progression of PCSCs into metastatic tumor cells.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

