Simvastatin reduces atherogenesis and promotes the expression of hepatic genes associated with reverse cholesterol transport in apoE-knockout mice fed high-fat diet
- PMID: 21241519
- PMCID: PMC3031258
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-8
Simvastatin reduces atherogenesis and promotes the expression of hepatic genes associated with reverse cholesterol transport in apoE-knockout mice fed high-fat diet
Abstract
Background: Statins are first-line pharmacotherapeutic agents for hypercholesterolemia treatment in humans. However the effects of statins on atherosclerosis in mouse models are very paradoxical. In this work, we wanted to evaluate the effects of simvastatin on serum cholesterol, atherogenesis, and the expression of several factors playing important roles in reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) in apoE-/- mice fed a high-fat diet.
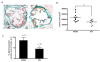
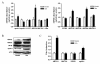
Results: The atherosclerotic lesion formation displayed by oil red O staining positive area was reduced significantly by 35% or 47% in either aortic root section or aortic arch en face in simvastatin administrated apoE-/- mice compared to the control. Plasma analysis by enzymatic method or ELISA showed that high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) and apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) contents were remarkably increased by treatment with simvastatin. And plasma lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) activity was markedly increased by simvastatin treatment. Real-time PCR detection disclosed that the expression of several transporters involved in reverse cholesterol transport, including macrophage scavenger receptor class B type I, hepatic ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters ABCG5, and ABCB4 were induced by simvastatin treatment, the expression of hepatic ABCA1 and apoA-I, which play roles in the maturation of HDL-C, were also elevated in simvastatin treated groups.
Conclusions: We demonstrated the anti-atherogenesis effects of simvastatin in apoE-/- mice fed a high-fat diet. We confirmed here for the first time simvastatin increased the expression of hepatic ABCB4 and ABCG5, which involved in secretion of cholesterol and bile acids into the bile, besides upregulated ABCA1 and apoA-I. The elevated HDL-C level, increased LCAT activity and the stimulation of several transporters involved in RCT may all contribute to the anti-atherosclerotic effect of simvastatin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Triacetyl-3-hydroxyphenyladenosine, a derivative of cordycepin, attenuates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012 Nov;237(11):1262-72. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2012.011401. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012. PMID: 23239437
-
Hydrogen decreases athero-susceptibility in apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins and aorta of apolipoprotein E knockout mice.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Mar;221(1):55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.11.043. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22209213
-
The combination of L-4F and simvastatin stimulate cholesterol efflux and related proteins expressions to reduce atherosclerotic lesions in apoE knockout mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2013 Dec 8;12:180. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-180. Lipids Health Dis. 2013. PMID: 24314261 Free PMC article.
-
Foam cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23782937 Review.
-
Role of apoA-I, ABCA1, LCAT, and SR-BI in the biogenesis of HDL.J Mol Med (Berl). 2006 Apr;84(4):276-94. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0030-4. Epub 2006 Feb 25. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16501936 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel interleukin-2-based fusion molecule, HCW9302, differentially promotes regulatory T cell expansion to treat atherosclerosis in mice.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 25;14:1114802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1114802. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36761778 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of statins on the organs: similar or contradictory?J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2017;9(2):64-70. doi: 10.15171/jcvtr.2017.11. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2017. PMID: 28740624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging and vascular dysfunction: beneficial melatonin effects.Age (Dordr). 2013 Feb;35(1):103-15. doi: 10.1007/s11357-011-9336-z. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Age (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 22109832 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Role of Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis: Novel Directions for Diagnosis and Targeting Therapy.Aging Dis. 2022 Apr 1;13(2):491-520. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0929. eCollection 2022 Apr. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 35371605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cordyceps militaris-Derived Polysaccharide CM1 Alleviates Atherosclerosis in LDLR(-/-) Mice by Improving Hyperlipidemia.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Dec 13;8:783807. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.783807. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34966782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glomset JA. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968;9:155–167. - PubMed
-
- Guan JZ, Tamasawa N, Murakami H, Matsui J, Tanabe J, Matsuki K, Yamashita M, Suda T. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, simvastatin improves reverse cholesterol transport in type 2 diabetic patients with hyperlipidemia. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2008;15:20–25. - PubMed
-
- Ly H, Francone OL, Fielding CJ, Shigenaga JK, Moser AH, Grunfeld C, Feingold KR. Endotoxin and TNF lead to reduced plasma LCAT activity and decreased hepatic LCAT mRNA levels in Syrian hamsters. J Lipid Res. 1995;36:1254–1263. - PubMed
-
- Ayaori M, Sawada S, Yonemura A, Iwamoto N, Ogura M, Tanaka N, Nakaya K, Kusuhara M, Nakamura H, Ohsuzu F. Glucocorticoid receptor regulates ATP-binding cassette transporter-A1 expression and apolipoprotein-mediated cholesterol efflux from macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:163–168. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000193513.29074.52. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

