The Zea mays mutants opaque-2 and opaque-7 disclose extensive changes in endosperm metabolism as revealed by protein, amino acid, and transcriptome-wide analyses
- PMID: 21241522
- PMCID: PMC3033817
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-41
The Zea mays mutants opaque-2 and opaque-7 disclose extensive changes in endosperm metabolism as revealed by protein, amino acid, and transcriptome-wide analyses
Abstract
Background: The changes in storage reserve accumulation during maize (Zea mays L.) grain maturation are well established. However, the key molecular determinants controlling carbon flux to the grain and the partitioning of carbon to starch and protein are more elusive. The Opaque-2 (O2) gene, one of the best-characterized plant transcription factors, is a good example of the integration of carbohydrate, amino acid and storage protein metabolisms in maize endosperm development. Evidence also indicates that the Opaque-7 (O7) gene plays a role in affecting endosperm metabolism. The focus of this study was to assess the changes induced by the o2 and o7 mutations on maize endosperm metabolism by evaluating protein and amino acid composition and by transcriptome profiling, in order to investigate the functional interplay between these two genes in single and double mutants.
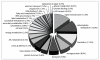
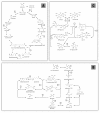
Results: We show that the overall amino acid composition of the mutants analyzed appeared similar. Each mutant had a high Lys and reduced Glx and Leu content with respect to wild type. Gene expression profiling, based on a unigene set composed of 7,250 ESTs, allowed us to identify a series of mutant-related down (17.1%) and up-regulated (3.2%) transcripts. Several differentially expressed ESTs homologous to genes encoding enzymes involved in amino acid synthesis, carbon metabolism (TCA cycle and glycolysis), in storage protein and starch metabolism, in gene transcription and translation processes, in signal transduction, and in protein, fatty acid, and lipid synthesis were identified. Our analyses demonstrate that the mutants investigated are pleiotropic and play a critical role in several endosperm-related metabolic processes. Pleiotropic effects were less evident in the o7 mutant, but severe in the o2 and o2o7 backgrounds, with large changes in gene expression patterns, affecting a broad range of kernel-expressed genes.
Conclusion: Although, by necessity, this paper is descriptive and more work is required to define gene functions and dissect the complex regulation of gene expression, the genes isolated and characterized to date give us an intriguing insight into the mechanisms underlying endosperm metabolism.
Figures




References
-
- Motto M, Thompson R, Salamini F. In: Cellular and Molecular Biology of Plant Seed Development. Larkins BA, Vasil IK, editor. 1997. Genetic regulation of carbohydrate and protein accumulation in seeds.
-
- Coleman CE, Larkins BA. In: Seed Proteins. Casey R, Shewry PR, editor. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands; 1998. Prolamines of maize.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

