Midterm results with thoracic endovascular aortic repair for chronic type B aortic dissection with associated aneurysm
- PMID: 21241855
- PMCID: PMC3688644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.10.043
Midterm results with thoracic endovascular aortic repair for chronic type B aortic dissection with associated aneurysm
Abstract
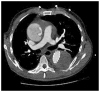
Objective: Thoracic endovascular aortic repair for chronic type B aortic dissection with associated descending thoracic aneurysm remains controversial. Concerns include potential ischemic complications due to branch vessel origin from the chronic false lumen and continued retrograde false lumen/aneurysm sac pressurization via fenestrations distal to implanted endografts. The present study examines midterm results with thoracic endovascular aortic repair for chronic (>2 weeks) type B aortic dissection with associated aneurysm to better understand the potential role of thoracic endovascular aortic repair for this condition.
Methods: Between March 2005 and December 2009, 51 thoracic endovascular aortic repair procedures were performed at a single institution for management of chronic type B dissection. The indication for thoracic endovascular aortic repair was aneurysm in all cases. A subset of 7 patients (14%) underwent placement of the EndoSure wireless pressure measurement system (CardioMEMS, Inc, Atlanta, Ga) in the false lumen adjacent to the primary tear for monitoring aneurysm sac/false lumen pulse pressure after thoracic endovascular aortic repair.
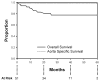
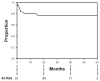
Results: Mean patient age was 57±12 years (range, 30-82 years); 14 patients (28%) were female. Mean aortic diameter was 6.2±1.4 cm. There were no in-hospital/30-day deaths, strokes, or permanent paraplegia/paresis. There were no complications related to compromise of downstream branch vessels arising from the false lumen. Two patients (3.9%) who had preexisting ascending aortic dilation had retrograde acute type A aortic dissection; both were repaired successfully. Median postoperative length of stay was 4 days. Mean follow-up is 27.0±16.5 months (range, 2-60 months). Actuarial overall survival is 77.7% at 60 months with an actuarial aorta-specific survival of 98% over this same time period. Actuarial freedom from reintervention is 77.3% at 60 months. All patients with the EndoSure wireless pressure measurement system exhibited a decrease in aneurysm sac/false lumen pulse pressure indicating a depressurized false lumen. The aneurysm sac/false lumen pulse pressure ratio decreased from 52%±27% at the predischarge measurement to 14%±5% at the latest follow-up reading (P=.029).
Conclusions: Thoracic endovascular aortic repair for chronic type B dissection with associated aneurysm is safe and effective at midterm follow-up. Aneurysm sac/false lumen pulse pressure measurements demonstrate a significant reduction in false lumen endotension, thus ruling out clinically significant persistent retrograde false lumen perfusion and provide proof of concept for a thoracic endovascular aortic repair-based approach. Longer-term follow-up is needed to determine the durability of thoracic endovascular aortic repair for this aortic pathology.
Copyright © 2011 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Trimarchi S, Nienaber CA, Rampoldi V, Myrmel T, Suzuki T, Bossone E, et al. Role and results of surgery in acute type B aortic dissection. Insights from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD) Circulation. 2006;114:I-357–64. - PubMed
-
- Tsai TT, Fattori R, Trimarchi S, Isselbacher E, Myrmel T, Evangelista A, et al. Long-term survival in patients presenting with type B acute aortic dissection. Insights from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. Circulation. 2006;114:2226–31. - PubMed
-
- Parsa CJ, Hughes GC. Surgical options to contend with thoracic aortic pathology. Semin Roentgenol. 2009;44:29–51. - PubMed
-
- Svensson LG, Kouchoukos NT, Miller DC, Bavaria JE, Coselli JS, Curi MA, et al. Expert consensus document on the treatment of descending thoracic aortic disease using endovascular stent-grafts. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:S1–41. - PubMed
-
- Crawford ES. The diagnosis and management of aortic dissection. JAMA. 1990;264:2537–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

