Disease activity score-driven therapy versus routine care in patients with recent-onset active rheumatoid arthritis: data from the GUEPARD trial and ESPOIR cohort
- PMID: 21242235
- PMCID: PMC3048626
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.137695
Disease activity score-driven therapy versus routine care in patients with recent-onset active rheumatoid arthritis: data from the GUEPARD trial and ESPOIR cohort
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the efficacy of disease activity score in 28 joints (DAS28ESR)-driven therapy with anti-tumour necrosis factor (patients from the GUEPARD trial) and routine care in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis (patients of the ESPOIR cohort).
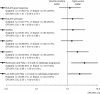
Results: After matching GUEPARD and ESPOIR patients on the basis of a propensity score and a 1:2 ratio, at baseline all patients had comparable demographic characteristics, rheumatoid factor, anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibody positivity and clinical disease activity parameters: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, mean DAS (6.26±0.87), Sharp/van der Heijde radiographic score (SHS), health assessment questionnaire (HAQ). Disease duration was longer in GUEPARD patients (5.6±4.6 vs 3.5±2.0 months, p<0.001). After 1 year, the percentage of patients in remission with an HAQ (<0.5) and an absence of radiological progression was higher in the tight control group (32.3% vs 10.2%, p=0.011) as well as the percentage of patients in low DAS with an HAQ (<0.5) and an absence of radiological progression (36.1% vs 18.9%, p=0.045). However, there was no difference in the decrease in DAS, nor in the percentage of EULAR (good and moderate), ACR20, ACR50 and ACR70 responses. More patients in the tight control group had an HAQ below 0.5 (70.2% vs 45.2%, p=0.005). Overall, pain, patient and physician assessment and fatigue decreased more in the tight control group. The mean SHS progression was similar in the two groups as was the percentage of patients without progression.
Conclusions: In patients with recent onset active rheumatoid arthritis, a tight control of disease activity allows more patients to achieve remission without disability and radiographic progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Nam JL, Winthrop KL, van Vollenhoven RF, et al. Current evidence for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of RA. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:976–86 - PubMed
-
- Knevel R, Schoels M, Huizinga TW, et al. Current evidence for a strategic approach to the management of rheumatoid arthritis with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:987–94 - PubMed
-
- Soubrier M, Puéchal X, Sibilia J, et al. Evaluation of two strategies (initial methotrexate monotherapy vs its combination with adalimumab) in management of early active rheumatoid arthritis: data from the GUEPARD trial. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:1429–34 - PubMed
-
- Combe B, Benessiano J, Berenbaum F, et al. The ESPOIR cohort: a ten-year follow-up of early arthritis in France: methodology and baseline characteristics of the 813 included patients. Joint Bone Spine 2007;74:440–5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials