A reduction in ATP demand and mitochondrial activity with neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 21242311
- PMCID: PMC3021997
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.072272
A reduction in ATP demand and mitochondrial activity with neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
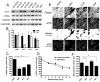
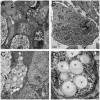
Here, we have investigated mitochondrial biology and energy metabolism in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and hESC-derived neural stem cells (NSCs). Although stem cells collectively in vivo might be expected to rely primarily on anaerobic glycolysis for ATP supply, to minimise production of reactive oxygen species, we show that in vitro this is not so: hESCs generate an estimated 77% of their ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Upon differentiation of hESCs into NSCs, oxidative phosphorylation declines both in absolute rate and in importance relative to glycolysis. A bias towards ATP supply from oxidative phosphorylation in hESCs is consistent with the expression levels of the mitochondrial gene regulators peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator (PGC)-1α, PGC-1β and receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140) in hESCs when compared with a panel of differentiated cell types. Analysis of the ATP demand showed that the slower ATP turnover in NSCs was associated with a slower rate of most energy-demanding processes but occurred without a reduction in the cellular growth rate. This mismatch is probably explained by a higher rate of macromolecule secretion in hESCs, on the basis of evidence from electron microscopy and an analysis of conditioned media. Taken together, our developmental model provides an understanding of the metabolic transition from hESCs to more quiescent somatic cell types, and supports important roles for mitochondria and secretion in hESC biology.
Figures
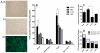
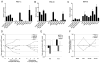
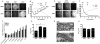



References
-
- Arany Z., Lebrasseur N., Morris C., Smith E., Yang W., Ma Y., Chin S., Spiegelman B. M. (2007). The transcriptional coactivator PGC-1beta drives the formation of oxidative type IIX fibers in skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 5, 35-46 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong L., Hughes O., Yung S., Hyslop L., Stewart R., Wappler I., Peters H., Walter T., Stojkovic P., Evans J., et al. (2006). The role of PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK and NFkappabeta signalling in the maintenance of human embryonic stem cell pluripotency and viability highlighted by transcriptional profiling and functional analysis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 1894-1913 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong L., Tilgner K., Saretzki G., Atkinson S. P., Stojkovic M., Moreno R., Przyborski S., Lako M. (2010). Human induced pluripotent stem cell lines show similar stress defence mechanisms and mitochondrial regulation to human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 28, 661-673 - PubMed
-
- Becker K. A., Ghule P. N., Therrien J. A., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., van Wijnen A. J., Stein G. S. (2006). Self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells is supported by a shortened G1 cell cycle phase. J. Cell. Physiol. 209, 883-893 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

