NF-κB in immunobiology
- PMID: 21243012
- PMCID: PMC3193440
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2011.13
NF-κB in immunobiology
Abstract
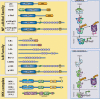
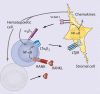
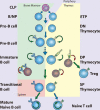
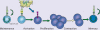
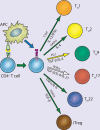
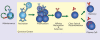
NF-κB was first discovered and characterized 25 years ago as a key regulator of inducible gene expression in the immune system. Thus, it is not surprising that the clearest biological role of NF-κB is in the development and function of the immune system. Both innate and adaptive immune responses as well as the development and maintenance of the cells and tissues that comprise the immune system are, at multiple steps, under the control of the NF-κB family of transcription factors. Although this is a well-studied area of NF-κB research, new and significant findings continue to accumulate. This review will focus on these areas of recent progress while also providing a broad overview of the roles of NF-κB in mammalian immunobiology.
Figures


References
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, West AP, Ghosh S. NF-kappaB and the immune response. Oncogene. 2006;25:6758–6780. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S, Hayden MS. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:837–848. - PubMed
-
- Burkly L, Hession C, Ogata L, et al. Expression of relB is required for the development of thymic medulla and dendritic cells. Nature. 1995;373:531–536. - PubMed
-
- Irla M, Hugues S, Gill J, et al. Autoantigen-specific interactions with CD4+ thymocytes control mature medullary thymic epithelial cell cellularity. Immunity. 2008;29:451–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

