Soft drink, software and softening of teeth - a case report of tooth wear in the mixed dentition due to a combination of dental erosion and attrition
- PMID: 21243073
- PMCID: PMC3020588
- DOI: 10.2174/1874210601004010198
Soft drink, software and softening of teeth - a case report of tooth wear in the mixed dentition due to a combination of dental erosion and attrition
Abstract
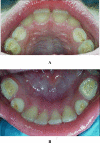
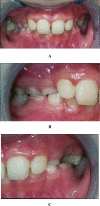
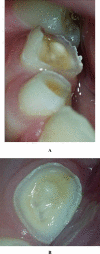
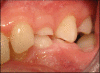
This case report describes a 9-year-old boy with severe tooth wear as a result of drinking a single glass of soft drink per day. This soft drink was consumed over a period of one to two hours, while he was gaming intensively on his computer. As a result, a deep bite, enamel cupping, sensitivity of primary teeth and loss of fillings occurred. Therefore, dentists should be aware that in patients who are gaming intensively, the erosive potential of soft drinks can be potentiated by mechanical forces leading to excessive tooth wear.
Keywords: Erosion; attrition.; soft drink; tooth wear.
Figures
References
-
- Ten Cate JM, Imfeld T. Dental erosion, summary. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996;104:241–4. - PubMed
-
- Addy M, Shellis RP. Interaction between attrition, abrasion and erosion in tooth wear. Monogr Oral Sci. 2006;20:17–31. - PubMed
-
- O’Sullivan E, Milosevic A. UK national clinical guidelines in paediatric dentistry: diagnosis, prevention and management of dental erosion. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2008;18(suppl 1):29–38. - PubMed
-
- Deery C, Wagner ML, Longbottom C, Simon R, Nugent ZJ. The prevalence of dental erosion in a United Sates and a United Kingdom sample of adolescents. Pediatr Dent. 2000;22:505–10. - PubMed
-
- Nunn JH, Gordon PH, Morris AJ, Pine CM, Walker A. Dental erosion: changing prevalence? a review of British national childrens surveys. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2003;13:98–105. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
