The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) and a single screening question as screening tools for depressive disorder in Dutch advanced cancer patients
- PMID: 21243377
- PMCID: PMC3244603
- DOI: 10.1007/s00520-010-1082-8
The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) and a single screening question as screening tools for depressive disorder in Dutch advanced cancer patients
Abstract
Purpose: Depression is highly prevalent in advanced cancer patients, but the diagnosis of depressive disorder in patients with advanced cancer is difficult. Screening instruments could facilitate diagnosing depressive disorder in patients with advanced cancer. The aim of this study was to determine the validity of the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) and a single screening question as screening tools for depressive disorder in advanced cancer patients.
Methods: Patients with advanced metastatic disease, visiting the outpatient palliative care department, were asked to fill out a self-questionnaire containing the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) and a single screening question "Are you feeling depressed?" The mood section of the PRIME-MD was used as a gold standard.
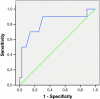
Results: Sixty-one patients with advanced metastatic disease were eligible to be included in the study. Complete data were obtained from 46 patients. The area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristics analysis of the BDI-II was 0.82. The optimal cut-off point of the BDI-II was 16 with a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 69%. The single screening question showed a sensitivity of 50% and a specificity of 94%.
Conclusions: The BDI-II seems an adequate screening tool for a depressive disorder in advanced cancer patients. The sensitivity of a single screening question is poor.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources