Direction and magnitude of nicotine effects on the fMRI BOLD response are related to nicotine effects on behavioral performance
- PMID: 21243486
- PMCID: PMC3083509
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-010-2145-8
Direction and magnitude of nicotine effects on the fMRI BOLD response are related to nicotine effects on behavioral performance
Abstract
Considerable variability across individuals has been reported in both the behavioral and fMRI blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) response to nicotine. We aimed to investigate (1) whether there is a heterogeneous effect of nicotine on behavioral and BOLD responses across participants and (2) if heterogeneous BOLD responses are associated with behavioral performance measures. In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study, 41 healthy participants (19 smokers)--drawn from a larger population-based sample--performed a visual oddball task after acute challenge with 1 mg nasal nicotine. fMRI data and reaction time were recorded during performance of the task. Across the entire group of subjects, we found increased activation in the anterior cingulate cortex, middle frontal gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, post-central gyrus, planum temporal and frontal pole in the nicotine condition compared with the placebo condition. However, follow-up analyses of this difference in activation between the placebo and nicotine conditions revealed that some participants showed an increase in activation while others showed a decrease in BOLD activation from the placebo to the nicotine condition. A reduction of BOLD activation from placebo to nicotine was associated with a decrease in reaction time and reaction time variability and vice versa, suggesting that it is the direction of BOLD response to nicotine which is related to task performance. We conclude that the BOLD response to nicotine is heterogeneous and that the direction of response to nicotine should be taken into account in future pharmaco-fMRI research on the central action of nicotine.
Figures



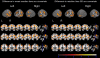
References
-
- Apud JA, Mattay V, Chen J, Kolachana BS, Callicott JH, Rasetti R, Alce G, Iudicello JE, Akbar N, Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Weinberger DR. Tolcapone improves cognition and cortical information processing in normal human subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007;32(5):1011–20. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301227. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Behrens T, Woolrich MW, Smith S. Multi-testing using a fully subject null hypothesis Bayesian framework: theory. New York City: Human Brain Mapping Meeting; 2003.
-
- Benowitz NL, Jacob P, 3rd, Jones RT, Rosenberg J. Interindividual variability in the metabolism and cardiovascular effects of nicotine in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982;221(2):368–72. - PubMed
-
- Bledowski C, Prvulovic D, Hoechstetter K, Scherg M, Wibral M, Goebel R, Linden LEJ. Localizing P300 generators in visual target and distractor processing: a combined event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci. 2004;24(42):9353–9360. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1897-04.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

